256-Bit Encryption
Cyber-criminals are always hunting for broken links in websites, security lapses in software codes or scripts, and loopholes in-network to penetrate and fulfill their evil desires. In this digital world, data security is of utmost importance, and hence business owners always prefer encryption security for the protection of their sensitive information to secure their digital business.
256 Bit Encryption: Is 256 Bit Encryption Safe?
Yes, as per current technology standards, 256 bit SSL encryption (AES) is considered a safe encryption strength. But when we talk about “256 bit encryption,” what does that term actually mean? Let’s break down what you need to know about 256 bit encryption and what kind of security it provides.
What is 256 Bit Encryption?
A 256 bit SSL encryption is a technique that uses 256 bit key to encrypt and decrypt the data transferred between the client and the server. The most modern forms of algorithms and protocols, including SSL and AES, uses 256 bit encryption for generating private and public security keys.
Encryption — the process of taking plaintext data and using an algorithm (also known as a cipher) to scramble it into an unrecognizable form known as a ciphertext — requires the use of encryption keys, which come in different sizes. So, when we talk about 256 bit encryption strength, it refers to both the length of the algorithm’s key that’s used to encrypt the data and its resistance to attacks. The larger the algorithm key size, the more difficult it is to crack using brute-force attacks.
In the old days when everything was written on paper, this required converting letters into something else. But when it comes to digital information — or any data stored on computers — these letters are stored in terms of binary digits, or “bits” of data, meaning 0s an 1s.
You might have seen “256-bit encryption” in any SSL/TLS certificate’s description. What this means is that it requires 2 256 different number combinations. That means it has about 115,792,089,237,316,195,423,570,985,008,687,907,853,269,984,665,640,564,039,457,584,007,913,129,639,936 possible combinations that you’d have to go through and start guessing one by one!
To decrypt a ciphertext that’s encrypted with 256 bit encryption without the corresponding private key, it would take 3.31 x 10 56 years!
Secure 256 Bit SSL Encryption
A secure 256 bit encryption technology is used to secure online communication between two nodes by encrypting the data with a 256 bit long key. Modern encryption protocols, including SSL/TLS and AES, use 256 bit encryption for building a secured communication channel.
Common Uses of 256 Bit Encryption
Considering that 256 bit encryption is considered the industry standard, it’s used in a lot of different ways. Some of the most common uses of 256-bit encryption are as follows:
- To generate symmetric session keys by browsers to start a secure SSL/TLS connection.
- To encrypt data in transit between a browser and a server.
- To encrypt data stored in an email to provide data at rest protection (if an email signing certificate is used).
- To encrypt the stored data on third-party cloud platforms like AWS, Google Drive, Dropbox, etc.
- To encrypt the sensitive data owned by the government and military.
How 256 Bit SSL Encryption Works
It shows the length of the encryption key. The data transferred between a users’ browser and the server of the website they’re visiting is encrypted using 256 bit encryption keys.
- When a user tries to access a website, the user’s browser selects the strongest encryption algorithm available between itself and server to create a random session key. 256-bit is the industry’s standard level of encryption strength and is what’s used to make the session key. The session key will used to encrypt and decrypt the data.
- The session key is encrypted using the website’s SSL certificate’s public key. The session key is encrypted using the 2048-bit key and sent to the website’s server.
- The server must possess the corresponding private key to decrypt the session key.
- Once the server decrypts the session key and gets access to it, the secure SSL connection starts between the browser and the server.
- Now, all the data in transit between the server and browser is encrypted and decrypted using the same session key. Session keys are symmetric i.e.; the same key is shared between a browser and server for that particular session. This key expires as soon as the session expires.
So, Is 256 Bit Encryption Safe?
256-bit encryption is one of the most secure technologies of the modern age that uses a 256-bit long key to encrypt and decrypt the data transferred between the server and the client. Security protocols, including AES and TLS/SSL, uses 256-bit encryption to generate private and public keys as a part of public key infrastructure (PKI).
All SSL/TLS certificates offer the same level of encryption regardless of brand, cost, or validation level. None of those things factor into the encryption strength. This means that a $10 domain validated (DV) SSL certificate offers the same encryption as a more expensive extended validation (EV) certificate.
The encryption strength you achieve with an SSL/TLS protocol depends on capabilities of the browser and server in question and how they’re configured. In some cases, 256 bit encryption may only provide a security level of 128 bits. So, if your server and the client’s browser are properly configured and capable of handling 256 bit encryption, then you can relax with the knowledge that any information passing between the two is as secure as possible.
Save 79% on SSL Security Certificates!
Get the lowest prices on trusted SSL certificates from Sectigo.
Encryption Resources
- Hashing vs Encryption — The Big Players of the Cyber Security World
- What Is Encryption and How Does It Work?
- Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption – 5 Things You Should Know
- SSL vs TLS: Decoding the Difference Between SSL and TLS
256-Bit Encryption
We sometimes use affiliate links in our content, when clicking on those we might receive a commission – at no extra cost to you. By using this website you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy.
What Does 256-Bit Encryption Mean?
256-bit encryption is a data/file encryption technique that uses a 256-bit key to encrypt and decrypt data or files.
Advertisements
It is one of the most secure encryption methods after 128- and 192-bit encryption, and is used in most modern encryption algorithms, protocols and technologies including AES and SSL.
Techopedia Explains 256-Bit Encryption
256-bit encryption is refers to the length of the encryption key used to encrypt a data stream or file. A hacker or cracker will require 2 256 different combinations to break a 256-bit encrypted message, which is virtually impossible to be broken by even the fastest computers.
Typically, 256-bit encryption is used for data in transit, or data traveling over a network or Internet connection. However, it is also implemented for sensitive and important data such as financial, military or government-owned data. The U.S. government requires that all sensitive and important data be encrypted using 192- or 256-bit encryption methods.
How Strong is 256-bit Encryption?
Cyber-criminals are always hunting for broken links in websites, security lapses in software codes or scripts, and loopholes in-network to penetrate and fulfill their evil desires. In this digital world, data security is of utmost importance, and hence business owners always prefer encryption security for the protection of their sensitive information to secure their digital business.
What Is AES 256-Bit Encryption?
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) 256-Bit Encryption defines the encryption key’s length used to encrypt the data. It indicates that if a hacker wants to decrypt data encrypted with 256-bit encryption, they need 256 different amalgamations to crack the data.
This is practically impossible to crack, and even the world’s supercomputers may require many years to get the combination by trying the trial-error method.
All the data communicated between browsers and websites are encrypted with 256-bit encryption. Even extremely sensitive financial data of government, military, or any other special departments, prefer AES-256-bit encryption methods rather than AES-128 or AES-192 block ciphers. All modern algorithms, security protocols, AES, and SSL, use 256-bit encryption security, as they find it extremely secured.
Though encryption is a too complex subject, the endpoint is that it jumbles the data and converts it into a non-readable coded format, which is difficult to decode or decipher.
More About Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is all about transforming data into an encrypted text by using algorithm functions. Here encrypted data is called ciphertext, whereas decrypted information is called plain text. Cryptographic keys help in the encryption-decryption process.
Example: A confidential message is encrypted by the sender using a key and decrypted by the receiver using another key.
There are 2 types of encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric Encryption
Modern cryptography works on Asymmetric Encryption technology.
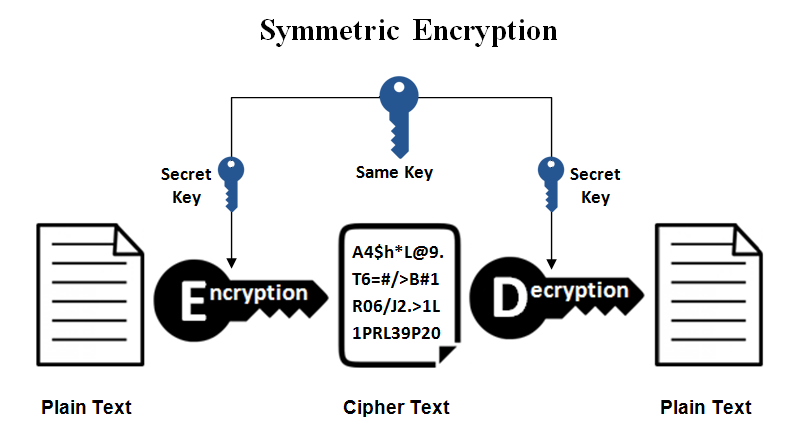
About Symmetric Encryption
In Symmetric Encryption, the encryption-decryption process takes place using just one key, i.e., only one key is used for encryption of data, and the same key decrypts the data as well.
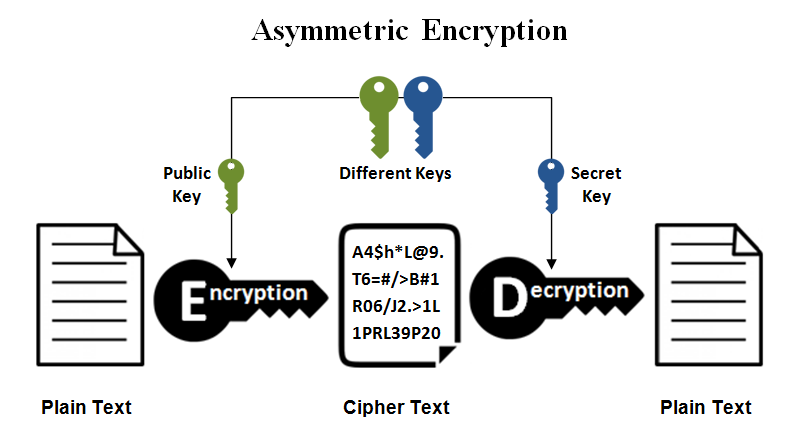
About Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric Encryption or Public-key Cryptography uses cryptographic keys to protect data. These two keys are utilized in the encryption-decryption process. They are the Public Key & the Private Key pairs.
The public key is used to encrypt data, and the private key is used for decryption of data. Though these keys are separate, they are mathematically connected.
How are the Keys produced?
Cryptographic algorithms use mathematical functions to generate a key pair. Here, the main point is that both the keys are created simultaneously, using an algorithm, and hence they are related to each other.
How does Asymmetric Encryption Work?
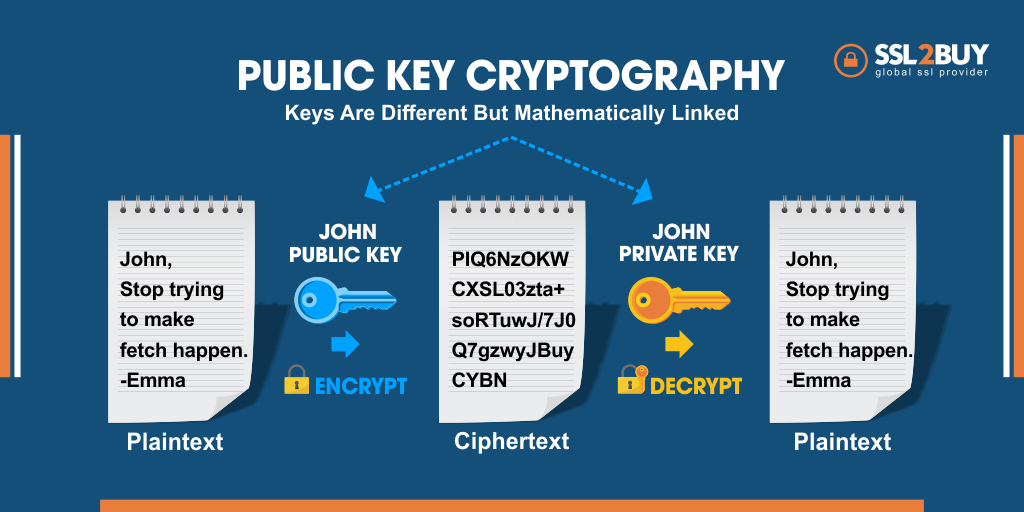
The below image is a perfect example of the functioning of Asymmetric Encryption.
Example: In the above image, John is trying to send secret messages to Emma, by sending the text in an encrypted format. He already has two keys (private key and public key) with him. With the help of Public Key, he encrypted the text and sent it to Emma with the Private Key. Emma will decrypt the text with the Private Key sent by John and read the message.
The public key can be shared with many people, but the private key needs to be shared with the recipient only.
Since Asymmetric keys are larger than Symmetric keys, data that is why encrypted with asymmetric keys is more robust, and hence decoding this data is an arduous task.
Public-Key Cryptography is used in SSL/TLS, Bitcoin, and Authentications, etc. This modern encryption method is an impenetrable method of communication.
How is Asymmetric Encryption Involved in SSL/TLS certificates?
All SSL/TLS certificates provide 256-Bit Encryption Security and work on both encryption methods stated above. Symmetric encryption is a quick process, whereas Asymmetric Encryption takes some more time.
When you visit any secured HTTPS site, your browser promptly creates asymmetric encryption with that website. Your web browser obtains the SSL certificate’s public key installed on the website.
It is this public key that encrypts the information sent to the website. The same will be decrypted with the private key. Never share the private key with anyone and store it in a secured location, accessed by authorized personnel only.
Common Uses of 256 Bit Encryption
256-Bit encryption is the industry-standard encryption, and hence there are multiple uses for the same.
- Generation of symmetric session keys by browsers for starting a secure SSL/TLS connection
- Encryption of data-in-transit between a browser and a server
- Encryption of storage of data in an email when an email signing certificate is used
- Encryption of stored data on third-party cloud platforms like Google Drive, Dropbox, AWS, etc.
- Encryption of sensitive data owned by the government and defences.
How 256 Bit SSL Encryption Works?
Unlike humans, computers do not store data in the form of alphabets; they store data in binary forms of 1’s and 0’s. This encoded language (raw form) is read by the computers, which further gets encrypted. This encryption used in SSL/TLS certificates.
Various file formats use different SSL Certificates, and hence encoding styles differ.
Process
- While accessing a website, the user’s browser chooses the encryption algorithm between itself and the webserver to create a random session key. The session key is made from 256-bit encryption strength. This key is used to encode and decode the data.
- The public key of the SSL certificate installed on the website encrypts the session key and is later sent to the webserver.
- The server already has the private key for decrypting the session key.
- After the server decrypts the session key, a secured connection is established between the browser and the server.
- All the data communicated between browser and server is later encrypted and decrypted using a single session key, as session keys are symmetric. When the session expires, the key also expires.
Is 256-Bit Encryption Secure?
256-bit encryption is the key length, which is used for encrypting data. You can make any combinations of two, from the power of 256, i.e., 2256 different combinations. With uncountable combinations, it is almost impossible to calculate the key combination.
Even brute forces take years to penetrate through 256-bit encryption security. Hence 256-bit encryption is the most reliable encryption technique to date.
Organizations with sensitive data opt for 256-bit encryption security for data integrity.
This confirms the reliability and strength of 256-bit encryption.
Wrapping Up:
Sometimes the security level of 256-bit encryption maybe only up to 128-bit encryption. Sometimes key size and security levels are interlinked, which may cause this issue.
Still, a hacker may never be able to crack the 256-bit symmetric key, because, in the time taken to break the same, the key may either have been discarded or the SSL certificate which generated the key may be replaced. So, in a nutshell, 256-bit encryption is strong and secure, thus protecting your digital world from cyber-criminals’ outrage.
Quick Links
- Free SSL Testing Tools
- Download Free Site Seal
- SSL Discount Offers