What Is a VPN and How Does It Work
You can’t prevent identity theft. No one can. Some security aspects — like a data breach at an organization where you have an account — are out of your control. But a VPN can help safeguard the information you send from and receive on your devices.
What Is a VPN?
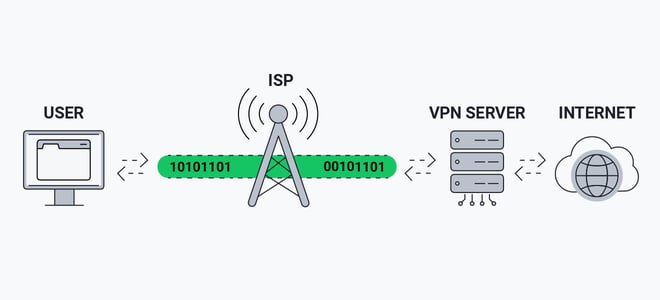
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) adds security and anonymity to users when they connect to web-based services and sites. A VPN hides the user’s actual public IP address and “tunnels” traffic between the user’s device and the remote server. Most users sign up for a VPN service online anonymity to avoid being tracked, and they often use public Wi-Fi where increased risks threaten the safety of their data.
Cybersecurity Education and Training Begins Here
Here’s how your free trial works:
- Meet with our cybersecurity experts to assess your environment and identify your threat risk exposure
- Within 24 hours and minimal configuration, we’ll deploy our solutions for 30 days
- Experience our technology in action!
- Receive report outlining your security vulnerabilities to help you take immediate action against cybersecurity attacks
Fill out this form to request a meeting with our cybersecurity experts.
Thank you for your submission.
Why Do I Need a VPN?
When you make a connection to a web server, your browser performs a lookup on the domain name from Domain Name Services (DNS) servers, gets the IP address, and then connects to the server. In most cases, the connection is encrypted using SSL/TLS. Even with SSL/TLS, numerous attacks on public Wi-Fi are possible. For example, a clever attacker can perform a downgrade on the version of TLS used to encrypt data, making communication vulnerable to brute force.
With a VPN added to the connection, the VPN service packages data in its own encryption and sends it across the network. The targeted server sees the VPN’s public IP address instead of the user’s public IP address. Should an attacker hijack the connection and eavesdrop on data, good VPN encryption eliminates the possibility of a brute force opportunity, which discloses data in a cryptographically insecure connection.
How to Use a VPN
The first step in VPN setup is finding a provider that’s right for you. Several VPN providers are available, but each one has its pros and cons. For example, you need a provider with a protocol that all devices support. It should be easy to set up, available from any geolocation, and provide cryptographically secure encryption for adequate security in public Wi-Fi use.
A main differentiating factor between a good VPN and one that offers little advantages is the number of users on a single IP address. Some service providers block VPN IP addresses because spammers and malicious threat actors also use VPN to anonymize their connection. Service providers can download a list of VPN IP addresses and block them from accessing local services. Good VPN offers private IP addresses, which costs more but also offers increased freedom and anonymity on the Internet.
After you choose a VPN, you then must configure your device to use it. These configurations are specific to each VPN provider, so yours equip you with their step-by-step instructions. Some VPN providers give you an install file to help with the setup process, which is helpful if you are unfamiliar with operating-system configurations.
How VPN Works
A VPN is an intermediary between your computer and the targeted server. Instead of relying on a browser to encrypt communication between your device and the server, the VPN adds its own encryptions and routes communication via its own servers. You often hear the term “tunneling” when it comes to VPN services. The idea is that the VPN service opens a “tunnel” between you and the targeted server. Then, the VPN sends your data through its “tunnel” so that no one else on the network can eavesdrop and hijack your data.
Technically, the VPN sets up a connection where your device communicates on the VPN network instead of the local network, including public Wi-Fi. You authenticate with the VPN server using your stored credentials and then receive a connection to the VPN servers. With the tunnel set up, you use a virtual network connection between you and the VPN server that encrypts and protects data from eavesdroppers. If you use an SSL/TLS connection, the data is encrypted and then encrypted again using the VPN service. It adds double encryption to your communication, improving the security of your data.
Remember, when connected to a VPN server, the IP address shown to the target server is the VPN server’s IP address. If the VPN server is virtually or physically located in another country, the target web server will identify your location as the VPN country location.
How to Set Up a VPN
To set up a VPN, you need to configure the operating system to use it instead of simply using the browser. Once configured, any connection to the Internet and remote web services will use the VPN server. The settings used to connect to the VPN server depend on the service that you choose. To set up a VPN in Windows, follow these steps.
Type “VPN” into the search bar, and the VPN settings window opens.
What Is a VPN and How Does It Work?
A VPN establishes a secure connection to the internet by creating a private tunnel through which encrypted data travels safely between your device and the VPN server, making that data unreadable to anyone else. A VPN protects your personal data and privacy online, and it hides your IP address, online activity, and communications. Strengthen your privacy right now by downloading a powerful and lightning-fast VPN.
Get it for Android, iOS, Mac
Get it for iOS, Android, PC
Get it for PC, Mac, iOS
Get it for Mac, PC , Android
Copy article link
Link copied
Written by Ivan Belcic & Christina Edwards
Published on March 1, 2023
What does VPN stand for?
- A VPN is virtual because it creates a digital tunnel — there isn’t a physical cable that reaches from your device directly to the VPN server.
- A VPN is private because it encrypts your data and hides your IP address.
- A VPN is a network because it creates a connection between multiple computers — your device and the VPN server.
This article contains:
This article contains:
This article contains:
Strictly speaking, the VPN meaning refers only to the private network connection itself — the actual software app that manages your device’s VPN connection is technically called a VPN client — but the two cybersecurity terms are often used interchangeably.
How does a VPN work?
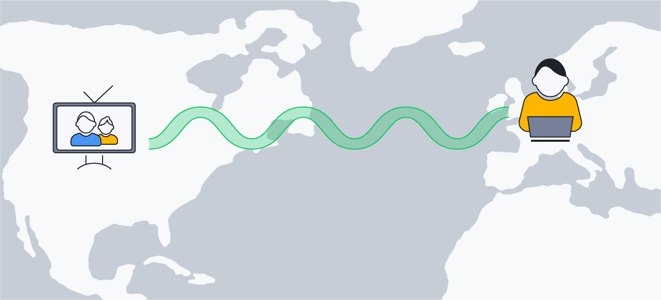
A VPN works by using encryption protocols to funnel all your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel — a virtual private network —between your computer and a remote VPN server. This hides your IP address and secures your data, preventing others from intercepting it.
When not hooked up to a VPN network, all your internet traffic is potentially exposed to your ISP, the government, advertisers, or other people on your network. That’s why VPN connections are crucial to your online privacy and security.
A VPN funnels your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel between your computer and a VPN server.
What is VPN tunneling?
VPN tunneling is the process of securing your device’s connection with a VPN server. A VPN server is a typical internet server configured with VPN software. Before being sent over the internet, all data is split into packets. At the core of VPN tunneling is a process called encapsulation. A VPN wraps an outer packet (a protocol) around the original data packet, encrypting it so it can’t be intercepted.
The level of protection you receive when using a VPN depends on the type of tunneling protocol used. It also depends on whether you use full or split tunneling — the main difference is defined by what traffic goes through the VPN. A full tunnel means all data goes through the VPN tunnel, whereas a split tunnel sends only traffic that you, or your employee, want to be protected (for example, Instagram activity could be exempt).
How do VPN servers operate?
Once the VPN tunnel is established, your device sends the VPN server encrypted information such as a website you want to visit. The VPN server decrypts this, hides your true IP address, and sends the data to the website’s server.
To the website, your IP address will appear to be the one attached to the VPN server. The VPN server then encrypts the data sent back by the web server and sends it on to you. When the website data arrives back at your device, your VPN client (VPN app) decrypts the data.
What does a VPN do?
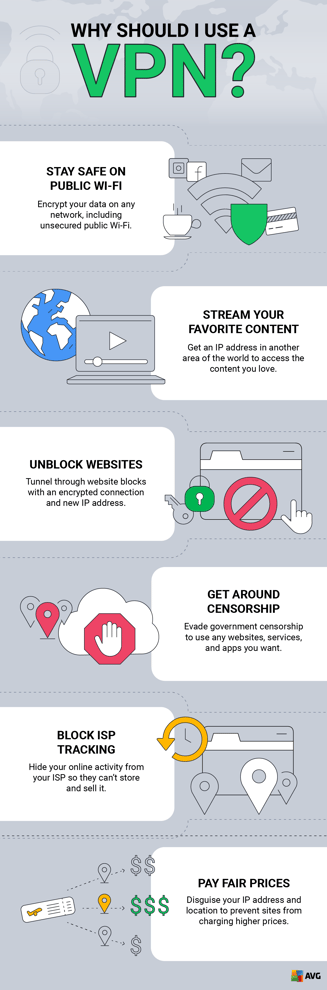
VPNs hide your IP address behind a different IP address (often in another country) provided by the VPN server. VPNs work by adding a layer of encryption to the data that passes through your internet connection. There are many benefits of using a VPN — VPNs let you:
- Encrypt your internet connection.
- Secure your data over public Wi-Fi networks.
- Stream freely and get around location-based content blocks.
- Access blocked websites.
- Avoid internet censorship.
- Evade ISP tracking.
- Prevent price discrimination.
Not only does a VPN connection encrypt your browsing and other web traffic, it can give you access to a freer internet by letting you configure your settings to alter your virtual online location. This combination of security and flexibility makes VPNs extremely versatile. Some people even use a VPN for gaming.
Having explained the VPN basics, let’s discuss what a VPN is used for in more detail. VPNs strengthen your personal security and privacy online because they help you do the following:
Encrypt your internet connection
VPNs establish a secure connection to the internet by encrypting all your online traffic and routing it through a point-to-point connectionbetween your device and the VPN server. Establishing an encrypted, private network is exactly what a VPN connection does — and this encrypted layer offers an array of security, privacy, and performance benefits.
When you’re hooked up to an encrypted VPN network, not only is all your internet data shielded from hackers and sniffers, but your true location and identity remain hidden from your internet service provider (ISP), the government, marketers, or anyone else who may be snooping on your local network.
Secure data transfer
If you log into your bank account, check your email, or use social media over an unsecured connection, hackers may be lurking, waiting to snap up your login credentials. And any messages you send or personal data you transmit can be intercepted and used for blackmail or identity theft.
Because a VPN connection encrypts your communication with its server, anyone trying to eavesdrop on the network will see only gibberish. That’s how a VPN ensures that no one can access your data. In fact, the original purpose of VPN technology was to connect remote workers with corporate networks, so that sensitive information could be shared safely.
Securing your data with a VPN is particularly important for staying safe on public Wi-Fi networks. Despite their convenience, there are many risks of public Wi-Fi, since anyone can hop onto an unsecured Wi-Fi network, and there’s no way to know exactly who’s connected at any given time (or what they’re doing). It’s all too easy for a hacker to sit on a public Wi-Fi network and intercept all the traffic flowing through it, which is known as a man-in-the-middle attack. Likewise, you should also use a VPN if you visit the dark web.
Stream from anywhere
Due to licensing restrictions, streaming platforms feature different content libraries in different countries around the world — this is known as geo-blocking. If you’re traveling abroad and want to keep up with your favorite shows from home, you may find that they’re unavailable in your current location.
A VPN lets you bypass location-based content blocks when watching TV online by letting you connect to the best server location to suit your needs. If you’re traveling and pick your home country from the server list, you’ll be able to access all the content you normally would. And you can even equip your mobile device with a VPN, meaning you can stream from anywhere, as well as prevent phone tracking.
A VPN lets you access shows from your home country when you’re traveling abroad.
Access blocked websites
You may find that certain websites are blocked for certain reasons or because you’re in a particular location — such as while you’re at school or at work. VPNs help you get around content blocks so you can access blocked websites, even if you’re somewhere that restricts access to certain sites.
Your encrypted VPN connection tunnels right through any restrictions to bring you the websites and services you want, regardless of the content blocks on your network.
Avoid censorship
Many countries limit internet access. China blocks Google and Facebook and all their associated services, such as Gmail, Google Maps, WhatsApp, and Instagram. A VPN connection can get you around censorship blocks in the same way it can circumvent content geo-blocking and website restrictions by reconfiguring your virtual IP address.
Evade ISP tracking
Without a VPN, your ISP can track all your online activity: the websites and services you use, when you use them, and how long you use them for. And ISPs can use that information to throttle your bandwidth depending on your usage.
Many people don’t understand how much leverage your ISP has over your data. In the UK, your ISP will store your online history for a year — that’s everything you read, watch, view, and click. And in the US, your ISP can store and sell your browsing history to the highest bidder — such as an advertising network, data broker, or subscription service — without your consent.
Because of how a VPN works, it protects you from this kind of invasion of privacy. Since VPNs encrypt your device’s internet connection, your ISP can’t monitor exactly what you’re doing online, and they can’t see your browsing history.
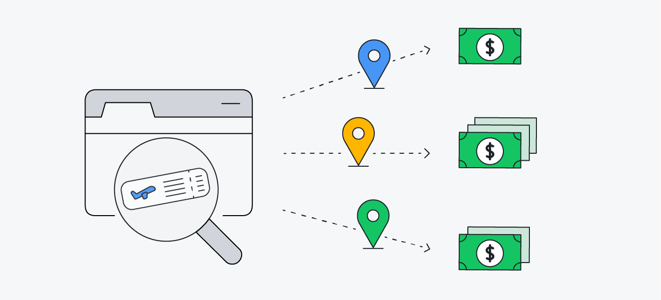
Prevent price discrimination
Price discrimination, also called dynamic pricing, happens when ecommerce sites offer different prices for the same product to different people based on their location or perceived ability to pay. Online retailers use a variety of criteria to calculate the prices for visitors to their websites — device type along with demographic information and your location.
Airlines are frequently accused of price discrimination, with flight prices changing depending on when you buy, where you are, and other factors. As well as allowing you to shop online more safely, using a virtual private network to give yourself an IP address in another country means you can counteract location-based price discrimination.
By keeping you anonymous, a VPN can shield you from price discrimination.
Why you should use a VPN
VPNs offer the best protection against online snoops and hackers, and you should use one if you want to browse privately. As well as encrypting your internet traffic, and keeping your online activity hidden, a VPN prevents anyone from finding your IP address by showing the public internet the IP address of the VPN server you’re using instead of your own.
Your public IP address links your device to your ISP as well as to your geographic location, which enables geo-blocking, censorship, price discrimination, and other content restrictions. Pair IP masking with encryption, and a VPN helps keep your online activities fully private from ISPs, hackers, and government surveillance. As more people are becoming aware of this, VPN usage is on the rise.
Here’s a list of folks who would benefit from using a VPN:
- People who use public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi doesn’t usually feature strong Wi-Fi security protocols, so whether you’re commuting or in a coffee shop you should use a VPN connection. Cybercriminals can all too easily intercept unsecured traffic, meaning your computer or phone could be hacked without you realizing it. - Businesses and employees
All businesses need to protect themselves from risks like costly ransomware attacks and other cyberthreats. And businesses need to protect the communications and data of remote workers. - Journalists and whistleblowers
Journalists who need to protect their sources, access secure data or records, or protect themselves from unwanted attention use VPNs to keep their digital activity private. - Citizens living under repressive regimes
Those who live in undemocratic states or in illiberal systems can use VPNs to access information more freely and get around government censorship. - Gamers
VPNs might help stop your ISP from throttling your bandwidth, which limits your internet speed. Or, you can use a VPN to access a game that isn’t available in your country. - Anyone accessing secure information
Whenever you access or enter sensitive data on the internet, from online banking to tax returns, keep your information private. - People traveling
Whether you’re overseas on business or vacation, you may want to access or stream content from your home country. - People who use ecommerce sites
Protect yourself from price discrimination, especially if you’re buying big-ticket items like flight tickets.
AVG Secure VPN enhances your privacy by masking you and other VPN users behind a single, shared IP address. That makes it extremely difficult for anyone to link your web activity back to you, since multiple users are sharing the same IP at any given time. It’s just one of the many ways AVG Secure VPN keeps you safe online.
What is a VPN?
A virtual private network (VPN) gives you online privacy and anonymity by creating a private network from a public internet connection. Learn more from Norton.
A virtual private network, better known as a VPN, gives you online privacy and anonymity by creating a private network from a public internet connection. VPNs mask your internet protocol (IP) address so your online actions are virtually untraceable. Most important, VPN services establish secure and encrypted connections to provide greater privacy than even a secured Wi-Fi hotspot.
A virtual private network is a key privacy tool that you should use when you’re logging onto the internet from a public place such as a coffee shop, hotel lobby, or any other spot that offers access to free public Wi-Fi.
A VPN creates a type of tunnel that hides your online activity, including the links you click or the files you download, so that cybercriminals, businesses, government agencies, or other snoops can’t see it.
Ready to find out more? Click on the links to jump to different topics, from a deeper understanding of VPN meaning to learning how to choose a VPN.
Why do you need a VPN service?
Surfing the web or transacting on an unsecured Wi-Fi network means you could be exposing your private information and browsing habits. That’s why a VPN should be a must for anyone concerned about their online security and privacy.
Ever log into your online bank account in your hotel’s lobby? Or maybe you’ve paid your credit card bill online while sipping a mocha at your favorite coffee shop. If you’ve done this without first logging onto a VPN, you could have exposed your private information and browsing habits to hackers and cybercriminals.
Unless you are logged into a private Wi-Fi network that requires a password, any data transmitted during your online sessions could be vulnerable to eavesdropping by strangers using the same network.
That’s where a VPN comes in: VPNs encrypt your data while online, scrambling it so that strangers can’t read it. The encryption that a VPN provides keep your online activities private, everything from sending emails and shopping online to paying bills or chatting with your doctor.
A VPN can also hide your IP address so that snoops don’t know that it’s you who is surfing the net, downloading files, and commenting on Reddit groups. How does this work? A VPN encrypts the data you send and receive on whatever device you’re using, including your phone, laptop, or tablet. It sends your data through a secure tunnel to the VPN service provider’s servers. Your data is encrypted and rerouted to whatever site you’re trying to reach.
What are the VPN basics?
A VPN enables you to connect to the internet in an encrypted fashion, which adds security and privacy to your online browsing. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi. That’s because it’s easier for identity thieves and other cybercriminals to eavesdrop on your online activity and steal the personal information you send and receive when you are using public Wi-Fi.
It gets worse. You may think you’re using the free public Wi-Fi provided at an airport, hotel, or coffee shop. But you may have logged onto a Wi-Fi network created by a cybercriminal. Once you’re on this network, the hacker can easily spy on your browsing and steal any personal information that you include in email messages or forum chats. If you log onto your online bank or credit card accounts, the cybercriminal might snag your log-in information.
A VPN, though, allows you to use inherently non-private public Wi-Fi by creating an encrypted tunnel through which your data is sent to a remote server operated by your VPN service provider. The VPN server then sends the data to the site you’re seeking to connect with, encrypted and safe from the prying eyes of identity thieves and other cybercriminals.
This isn’t to say that VPNs don’t come with challenges. They can sometimes slow your computer’s performance, especially if your VPN’s servers are geographically distant. For best performance, consider a VPN with servers located around the world. That way, your data can be routed through a closer location.
Some VPN services limit your usage. For instance, they may limit the amount of data you can send in a single connection or over a period of time. They might also limit the speed of the data. This can be common with free VPN services.
How does a VPN protect your IP address and privacy?
VPNs essentially create a data tunnel between your local network and an exit node in another location, which could be thousands of miles away, making it seem as if you’re in another place. This benefit allows online freedom, or the ability to access your favorite apps and websites while on the go.
Here’s a closer look at how a virtual private network works. VPNs use encryption to scramble data when it’s sent over a Wi-Fi network. Encryption makes the data unreadable. Data security is especially important when using a public Wi-Fi network, because it prevents anyone else on the network from eavesdropping on your internet activity.
There’s another side to privacy. Without a VPN, your internet service provider can know your entire browsing history. With a VPN, your search history is hidden. That’s because your web activity will be associated with the VPN server’s IP address, not yours. A VPN service provider may have servers all over the world. That means your search activity could appear to originate at any one of them. Keep in mind, search engines also track your search history, but they’ll associate that information with an IP address that’s not yours. Again, your VPN will keep your online activity private.
VPN privacy: What does a VPN hide?
A VPN can hide a lot of information that can put your privacy at risk. Here are five of them.
1. Your browsing history
It’s no secret where you go on the internet. Your internet service provider and your web browser can track just about everything you do on the internet. A lot of the websites you visit can also keep a history. Web browsers can track your search history and tie that information to your IP address.
Here are two examples why you may want to keep your browsing history private. Maybe you have a medical condition and you’re searching the web for information about treatment options. Guess what? Without a VPN, you’ve automatically shared that information and may start receiving targeted ads that could draw further attention to your condition.
Or maybe you just want to price airline tickets for a flight next month. The travel sites you visit know you’re looking for tickets and they might display fares that aren’t the cheapest available.
These are just a few isolated examples. Keep in mind your internet service provider may be able to sell your browsing history. Even so-called private browsers may not be so private.
2. Your IP address and location
Anyone who captures your IP address can access what you’ve been searching on the internet and where you were located when you searched. Think of your IP address as the return address you’d put on a letter. It leads back to your device.
Since a VPN uses an IP address that’s not your own, it allows you to maintain your online privacy and search the web anonymously. You’re also protected against having your search history gathered, viewed, or sold. Keep in mind, your search history can still be viewed if you are using a public computer or one provided by your employer,school, or other organization.
3. Your location for streaming
You might pay for streaming services that enable you to watch things like professional sports. When you travel outside the country, the streaming service may not be available. There are good reasons for this, including contractual terms and regulations in other countries. Even so, a VPN would allow you to select an IP address in your home country. That would likely give you access to any event shown on your streaming service. You may also be able to avoid data or speed throttling.
4. Your devices
A VPN can help protect your devices, including desktop computer, laptop, tablet, and smart phone from prying eyes. Your devices can be prime targets for cybercriminals when you access the internet, especially if you’re on a public Wi-Fi network. In short, a VPN helps protect the data you send and receive on your devices so hackers won’t be able to watch your every move.
5. Your web activity — to maintain internet freedom
Hopefully, you’re not a candidate for government surveillance, but who knows. Remember, a VPN protects against your internet service provider seeing your browsing history. So you’re protected if a government agency asks your internet service provider to supply records of your internet activity. Assuming your VPN provider doesn’t log your browsing history (some VPN providers do), your VPN can help protect your internet freedom.
How can a VPN help protect against identity theft?
Identity theft occurs when thieves steal your personal information and use it to commit crimes in your name — like taking over or opening new accounts, filing tax returns in your name, or renting or buying property. A VPN can help protect against identity theft by helping protect your data. It creates an encrypted tunnel for the data you send and receive that’s out of reach of cyberthieves.
If your smartphone’s Wi-Fi is enabled at all times, your device could be vulnerable without you ever knowing it. Everyday activities like online shopping, banking, and browsing can expose your information, making you vulnerable to cybercrime.
A VPN can protect the information you share or access using your devices. That’s especially important when using a public Wi-Fi network, where a cyberthief on the same network could capture your login credentials and the credit card number you type in when you shop online.
You can’t prevent identity theft. No one can. Some security aspects — like a data breach at an organization where you have an account — are out of your control. But a VPN can help safeguard the information you send from and receive on your devices.
Do you need a VPN at home?
If you’re logging onto the internet from your home? Do you need a VPN?
Probably not. When you established your home Wi-Fi network, it is likely that you protected your network with a password. Because of that, you may not need the added security of a VPN to shield your online activity.
Investing in a VPN for home use, then, might be a waste of money, unless you want to keep your web surfing private from your internet service provider (ISP) or if you choose to access streaming content or sports coverage that you couldn’t otherwise access from your location.
Tempted to invest in a VPN service provider for home internet access? You could do that, but it might not be a wise financial move. It’s worth noting you might consider a free VPN, but those services may cover their costs in other ways such as selling your data to third-parties for marketing purposes.
There are exceptions where you might consider using a VPN at home. You might want to use a VPN if you’re worried about your ISP tracking your online activity. If you connect to the internet through a VPN, the provider of your internet services won’t be able to see what you’re doing online.
However, the company that provides your VPN service will. If you trust that company more than your internet service provider, then using VPN at home might make sense.
There’s another reason to use VPN. It can help you stream content or watch sporting events that aren’t available in your location. Keep in mind you should understand any contractual agreements you’ve accepted with your streaming provider. Further, governmental regulations in other regions or countries might make this a bad idea.
What should you look for in VPN services?
The VPN market is crowded with options, so it’s important to consider your needs when you’re shopping for a VPN.
Think about what is important to you. Do you want to be able to surf the web anonymously by masking your IP address? Are you afraid that your information could be stolen on public Wi-Fi? Are you a frequent traveler who wants to be able to watch your favorite shows while you’re on the go.
A good VPN can help you check all three boxes, but here are some other points to consider.
How to choose a VPN
A smart way to stay secure when using public Wi-Fi is to use a VPN solution. But what’s the best way to choose a virtual private network? Here are some questions to ask when you’re choosing a VPN provider.
- Do they respect your privacy? The point of using a VPN is to protect your privacy, so it’s crucial that your VPN provider respects your privacy, too. They should have a no-log policy, which means that they never track or log your online activities.
- Do they run the most current protocol? OpenVPN provides stronger security than other protocols, such as PPTP. OpenVPN is an open-source software that supports all the major operating systems.
- Do they set data limits? Depending on your internet usage, bandwidth may be a large deciding factor for you. Make sure their services match your needs by checking to see if you’ll get full, unmetered bandwidth without data limits.
- Where are the servers located? Decide which server locations are important to you. If you want to appear as if you’re accessing the Web from a certain locale, make sure there’s a server in that country.
- Will you be able to set up VPN access on multiple devices? If you are like the average consumer, you typically use between three and five devices. Ideally, you’d be able to use the VPN on all of them at the same time.
- How much will it cost? If price is important to you, then you may think that a free VPN is the best option. Remember, however, that some VPN services may not cost you money, but you might “pay” in other ways,
such as being served frequent advertisements or having your personal information collected and sold to third parties. If you compare paid vs. free options, you may find that free VPNs:
- don’t offer the most current or secure protocols
- don’t offer the highest bandwidth and connection speeds to free users
- do have a higher disconnection rate
- don’t have as many servers in as many countries globally
- don’t offer support
There are many points to consider when you’re choosing a VPN, so do your homework to make sure you’re getting the right fit for your needs. Regardless of which provider you choose, rest assured that a good VPN will provide more security, privacy, and anonymity online than a public Wi-Fi hotspot can.
VPN product comparison
Which VPN provider is right for you? We can’t tell you that. But we can help you comparison shop. Here’s a look at some relevant factors to consider when hunting for a VPN provider and how some of the top VPN services rank when it comes to these key features.
We focused on these nine factors to consider when choosing a VPN. Click on the links if you want to skip ahead.
- VPN prices
- Are there free versions, and does it matter?
- Number of servers
- Number of locations and countries for servers
- Operating system support
- Does the provider offer mobile VPN?
- How many devices can connect to the VPN at once?
- Does the VPN block ads?
- Does the VPN have a kill switch?
- Does the VPN log user data?
VPN prices
It’s tempting to choose your VPN provider based on price. After all, we all want to spend as little as we can each month, right?
But focusing only on price could be a mistake. You want your VPN provider to protect your online privacy and encrypt the data you send and receive. You want it to be reliable. And you want fast connections. All of these factors are just as important — if not more so — than price.
That being said, most providers of VPN services charge similar prices, usually ranging from $9.99 to $12.99 a month, with some exceptions. When looking at prices, though, make sure to understand what you’re getting.
A provider, for instance, might charge you as low as $4.99 a month to provide VPN protection on one device. It might charge $9.99 a month, though, to provide the same service for 10 devices. You might also be able to reduce your monthly rate by signing up for a longer term. You’ll typically spend less on a monthly basis if you sign up for a yearlong VPN plan than if you elect to pay on a month-by-month basis.
Are there free versions, and does it matter?
Many of the top providers offer free versions of their VPNs. But the free versions may be limitations — for instance, on how much data you can use.
Some VPN providers offer free trials of their paid versions. The trials typically run for about a month. Some allow to access most of the VPN features of the paid service, although there may be data limitations.
If you sign up for a free trial, you provide the same personal and payment information you’d use if you were signing up for the paid service. You can cancel your account before the end of the trial. If you don’t cancel, the provider will begin to bill you for continuing service.
Keep in mind, some free VPNs may collect and share or sell your data to third parties for marketing purposes, while others may not block ads.
Number of servers
More important than price is the number of servers your VPN provider offers. In general, the more servers, the better.
Why? VPNs that don’t offer a high number of servers will often be plagued by slow online speeds. That can be a problem if you’re first connecting to a VPN and then downloading files or streaming videos.
If too many users are on the same server, that server can get overloaded. Once that happens, you’ll notice a slowdown in your browsing speed.
When looking at a VPN provider, then, make sure you sign up with one that does offer a high number of servers. How many servers is enough? There’s no one answer for that. But VPN services that boast 1,000 servers or more may be less likely to get overloaded.
Number of locations and countries for servers
Paid VPN providers will offer servers in several different countries. As an example, Norton Secure VPN has servers in 31 different countries.
Why does this matter? Having servers in different countries offers you more flexibility and could boost your connection speed. Usually, your internet speed will be greater if you are connecting to a server that is closer to you. When you choose a VPN provider, then, it makes sense to select one that has servers in your country.
There might be times when you want to connect to a server outside of your country. Maybe you live in a part of the world where the government censors the internet. By connecting to a VPN based in a country without this censorship, you can browse the web more freely. Even so, it might be smart to adhere to a particular government’s regulations and laws.
Or maybe you want to access online content that is only available in a country other than yours. If you connect through a server outside your country, the providers of this content won’t see that your actual IP address is coming from your home country. Keep in mind, though, you may be violating your user agreement of your content service.
Again, there is no right number of countries or locations for a VPN service. Instead, look for services that offer a large number of locations in a variety of countries. This will give you the most flexibility.
Operating system support
This is fairly self-explanatory: You want a VPN service that works with the operating systems on your laptop, smart phone, desktop or tablet. Fortunately, paid services tend to work on all the major operating systems. Finding a VPN provider that works with your devices’ operating systems, then, shouldn’t be difficult.
Does the provider offer mobile VPN?
You might understand that you need the privacy protection of a VPN when you’re accessing the web through your laptop or desktop. But many of us spend a lot of time visiting websites, watching videos, and playing online games through our mobile devices. Because of this, it’s important to rely on VPN services when using your mobile devices, too.
Fortunately, most major VPN providers — especially those that charge a fee — offer mobile services, too. All of the companies in our list, for example, do this. Finding a VPN service that can protect your phone and tablet, then, shouldn’t be a challenge.
How many devices can connect to the VPN at once?
Think of how many devices in your home connect to the internet. You have your laptops, tablets, smart phones, and voice assistants. You might even have smart appliances that access the web.
That’s why it’s important to work with a VPN provider that allows several devices to connect to it at one time. That way, you can have both your laptop and your children’s tablets routed through a VPN at the same time.
Some VPN providers might offer different plans that allow for a higher or lower number of simultaneous connections. In general, you can expect to pay more for a greater number of connections. Top providers allow you to connect 10 or more devices simultaneously.
Does the VPN block ads?
Pop-up ads can be annoying and dangerous. They can slow your browsing speeds and clutter your screen when you’re trying to watch videos or read a blog post. Even worse, cybercriminals often use pop-up ads — if you click on them — to infect your computer with malware.
That’s why ad blockers are so important: They help to keep these ads from showing up on your screen when you’re surfing the web. This can improve speed — web pages load faster when they’re not bogged down with ads — and help keep your devices safe from ads littered with malware.
You want a VPN service that blocks ads, then. Again, most paid services will do this. And you can see that each VPN provider in our list does block ads.
Does the VPN have a kill switch?
What if your connection with your VPN provider drops? Usually, your laptop, smartphone or other device will revert back to public Internet Protocol address provided by your home Internet Service Provider. This means that snoops could then be able to track your online activity and see your IP address until you connect back with your VPN provider.
Some VPN providers offer a kill switch feature to deal with this. If the VPN connection drops, the kill switch is designed to instantly sever your connection to the internet. This way, your IP address and online activity aren’t visible to anyone else.
Does the VPN log user data?
Paid VPN services usually promise that they won’t log your data. That’s a good thing: If your VPN provider is logging — or tracking — your activity online, what’s to stop it from one day sharing or selling your browsing history with businesses or government agencies?
The logging of data is why many tech experts recommend that consumers avoid free VPN services. These services might log your data and then sell them to others as a way to make money because they are not collecting monthly subscriptions.
Remember, the purpose of a VPN is to protect your online privacy. So it’s wise to consider a VPN provider that doesn’t log your data.
VPN glossary
Learning about VPNs may seem like it requires a specialized vocabulary. Here’s a glossary with definitions of some of the most common terms you’ll see.
AES encryption
Encryption is essential to helping keep your data unreadable by hackers, private companies, and possibly by government agencies. Encryption jumbles up your data so that others can’t make sense of it without the specific decryption key. AES, which stands for Advanced Encryption Standard, was an encryption method developed by Belgium cryptographers Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen. In 2002, AES became the U.S. federal standard for encryption. It has since become the standard form of encryption for the rest of the world, too.
Browser history
A record of all your internet activity using a particular web browser, including keywords you searched for and websites you accessed.
Geo-restrictions
One of the main reasons users rely on VPNs? They want to get around geo-restrictions. These restrictions are often put in place by entertainment companies that only want to distribute content to certain regions. For instance, Netflix might offer content in the United States that it doesn’t show in the UK. It might offer programming in the UK that Netflix users in the United States can’t access. By using a VPN with an IP address based in the UK, U.S. viewers can try to access Netflix programming that isn’t available in their home country. The VPN service — and the VPN connection — hides the location where the actual internet connection is made. Check your streaming service agreement for its Terms of Service, and also be mindful that some countries may have penalties for using VPN to circumvent its rules.
Google search history
A record of all your internet searches using the Google search engine.
IP address
IP stands for Internet Protocol, and an IP address is a series of numbers and periods that identifies a computer that’s using the Internet Protocol to send and receive data over a network.
Ipsec
IPsec is a series of protocols, or rules, that virtual private networks use to secure a private connection between two points, usually a device such as a laptop or smartphone and the Internet. Without these protocols, VPNs would not be able to encrypt data and ensure the data privacy of users. The name IPsec stands for Internet Protocol Security.
ISP
Short for Internet Service Provider, this is a service you pay for to connect to the internet. ISPs can record your browsing history and may be able to sell it to third parties, for marketing or other purposes.
Kill switch
Users sign up with a VPN provider for online privacy and data security. But what happens if a VPN provider’s network connection fails? Your computer or mobile device will default back to the public IP address provided by your ISP. This means that your online activity can now be tracked. A kill switch, though, prevents this from happening. If your VPN provider’s connection fails, the kill-switch feature severs your connection to the Internet completely. This way, your online activity won’t be monitored by others. Not all VPN providers offer this feature, so look for it when shopping around.
L2TP
The acronym L2TP stands for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol, and is a series of rules that allow internet service providers to allow for VPNs. L2TP on its own, though, does not encrypt data, so does not provide complete privacy for users. That’s why L2TP is usually used with IPsec to help protect the online privacy of users.
Public Wi-Fi
A wireless network in a public place that allows you to connect a computer or other device to the internet. Public Wi-Fi is often unprotected and potentially accessible to hackers.
Search engines
A service that allows you to search for information using keywords on the internet. Many popular search engines record your search history and can make money off that information.
Service provider
A company that provides a virtual private network — essentially routing your connection through a remote server and encrypting the data.
Simultaneous connections
You probably have plenty of devices connected to the internet at any one time, everything from your smartphone to your laptop to the desktop computer in your home office. Many VPN providers now offer protection for all your simultaneous internet connections with one account. This is important: You might think to log into a VPN before searching the internet on your laptop. But if your smartphone isn’t protected by a secure VPN, your browsing activity on that device won’t have protection.
Virtual private network
A VPN gives you online privacy and anonymity by creating a private network from a public internet connection. It masks your internet protocol address to keep your online actions private. It provides secure and encrypted connections to provide greater privacy and security for the data you send and receive.
VPN connection
A virtual private network connection allows you to access the internet through a remote server, hiding your actual location and browser history, and encrypting your data.
VPN privacy
This refers to the privacy that using a VPN provides. For instance, a VPN encrypts your data, disguises your location, and conceals your browsing history and the data you transmit via the internet.
VPN clients
A VPN client makes it easier for users to connect to a virtual private network. That’s because it is the actual software that is installed on your computer, phone or tablet. The most common operating systems, such as Android, Windows, and iOS, already come with VPN client software pre-installed. However, many users choose to work with third-party VPN clients that offer different features and user interfaces.
VPN protocols
VPN protocols are similar to a set of instructions. VPN providers use these protocols to make sure that users are able to connect securely to a virtual private network. There are several VPN protocols available, all with their own strengths and weaknesses. OpenVPN is one of the more popular protocols. Users like OpenVPN because it is secure and works with most operating systems. The biggest downside of OpenVPN? It can offer slower connection speeds than other protocols.
VPN provider
Synonymous with VPN service, this is a service you sign up for that allows you to connect to a virtual private network by providing a temporary IP address that hides your actual address.
VPN server
VPN services allow you to connect to the internet through remote servers that they either own or have access to. This disguises your location.
VPN service
A service you sign up for that allows you to connect to a virtual private network by providing a temporary IP ddress that hides your actual address.
VPN tunnel
You might sometimes hear your virtual private network referred to as a VPN tunnel. This is just another name for the encrypted connection between your device — a laptop, phone, tablet or desktop computer — and the internet. You can create a VPN tunnel at home or on public Wi-Fi. Once you are using a VPN tunnel to connect to the internet, your ISP, private companies, or the government can no longer see the sites you are browsing or the links you are clicking. A VPN tunnel also hides your IP address. Instead of showing your real location, the sites you surf will only register the location of the VPN provider with which you are working.
VPN web browser
A web browser that includes a built-in VPN service, allowing you to hide your browsing activity on the internet.
Web search history
A record of what you searched for on the internet. Your internet service provider and your web browser likely have a complete history of your internet search activity.
Wi-Fi
A wireless network using a radio frequency to connect your computer and other devices to the internet and each other.
VPN Frequently Asked Questions
What is a VPN in simple terms?
A virtual private network, better known as a VPN, protects your identity and browsing activity from hackers, businesses, government agencies, and other snoops. When connecting to the internet, your data and IP address are hidden by a type of virtual tunnel. This keeps others from spying on your online activity.
How does a VPN work?
When you sign up with a VPN provider, you first log onto that service before you connect to the internet. Once you are connected, others can’t see your activity. Your VPN provider will encrypt your data, scrambling it so that hackers, government agencies, and businesses can’t see what websites you visit, messages you send, social media sites you use, or files you download.
Is using a VPN safe?
A quality VPN is a safer way to search the internet. Without a VPN, your browsing and downloading activity could be visible to hackers, snoops, and cybercriminals. A hacker could intercept your email messages, mine personal data such as your Social Security number, or uncover the password to your online banking portal or credit card. Any of this could expose you to identity theft or fraud. That’s why logging onto a VPN, which protects your privacy, is one of the safest ways to browse the web.
Is a VPN legal?
VPNs are not illegal in the United States. However, not all countries have the same laws regarding these services. For instance, China, Russia, and North Korea either regulate or ban VPNs. You should know, too, that if you commit an illegal act online using a a VPN, that act is still illegal. Customers often use VPNs so that they can stream sporting events and TV shows that they may be blocked from accessing in their own region. Using a VPN to pretend that you are logging onto the internet from a different location might violate the service agreements of streaming services.
Are free VPNs safe?
You can choose from many free VPNs. This could be useful if you are on a limited budget. Be aware, though, that free VPN services might not provide the same type of browsing privacy that pay services offer. Free VPNs have to make money somehow. They might do this by tracking and collecting your browsing data and selling it to third parties, like advertisers. Others might hit you with a steady stream of online ads. Free VPNs might be easier on your wallet, but using one might compromise some of your privacy.
What are the disadvantages of a VPN?
There aren’t too many negatives of using a VPN. A possible one? A VPN could result in a slightly slower internet connection. That’s because a VPN encrypts the data you send and receive, which could result in a lag while you browse the internet or download files.
Should I use a VPN at home?
VPNs are especially useful when you are browsing the web through public Wi-Fi, whether you are at a coffee shop, hotel lobby, or public library. But a VPN can also protect your privacy when you’re at home, keeping your browsing safe from prying eyes. You can also use a VPN to access streaming content from your home that might be otherwise locked in your area.
Does a VPN hide your IP address?
With a VPN, you log onto the internet through another provider. This hides your actual IP address. If someone is trying to spy on your browsing activity, that person will only see the IP address of one of your provider’s servers, not yours.
Can you be tracked if you use a VPN?
Your VPN provider should both encrypt the data you send and receiveyour data and hide your IP address. This means that criminals, hackers, and others won’t be able to track your online activities. However, your internet service provider — also known as your ISP — can determine if you are using a VPN by looking at your IP address. If it doesn’t match, your provider will know that you are using a VPN when connecting to the internet. Fortunately, your internet service provider still won’t be able to track your browsing activity if you are using a VPN.
Should I leave my VPN on all the time?
If you want the most protection, you should leave your VPN on at all times. You should especially leave your VPN on when you are logging onto the internet using public Wi-Fi. These connections are notoriously unsecure, providing tempting targets for hackers and cybercriminals. You should also use a VPN whenever you are logging into your credit card or online banking accounts. You don’t want to expose this sensitive financial information to online thieves.
Can your internet provider see your history with a VPN?
If you connect to the internet through a VPN, your internet service provider can’t see your browsing history and downloads. That is one of the main benefits of a VPN: keeping your browsing history private from your internet service provider.
Does your VPN drain battery?
A VPN will consume more of your battery’s power when it is on. This can be a problem when you are using a VPN with your smartphone. Many VPNs do come with a “power saver” feature, though. This automatically turns your VPN off when your device’s screen turns off. Then, when you turn your device back on, the VPN automatically turns itself back on, too.
Is using a VPN safe for banking?
Because a VPN encrypts the data you send, such as when you enter your log-in credentials, it can protect you while you are visiting your bank’s online portal. Snoops won’t be able to see your log-in information if you first connect to a VPN. This is especially helpful if you must access your online bank through a public Wi-Fi connection. You should only do this in an emergency because such online connections are so vulnerable to hackers. But by logging onto public Wi-Fi through a VPN, you can block your browsing activity from cybercriminals, hackers, and other spies.
What are the types of VPN security protocols?
VPNs use a variety of different protocols. Older protocols, such as PPP and PPTP, are considered less secure. Here are some of the types of security protocols.
- IP Security (IP Sec). Internet Protocol Security is a popular protocol that protects data through either a transport mode or a tunnel mode. Both provide encryption. It’s considered highly secure and is useful for securing inbound and outbound traffic. But it can require a lot of processing power, and that can affect device performance. Also, some of the security algorithms used in IPSec in the past have been hacked by cybercriminals. Newer versions of IPSec use stronger, more complex algorithms.
- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)/IPSec. L2TP is a VPN protocol that doesn’t encrypt data by itself. That’s why it’s paired with IPSec encryption. One of its primary advantages? It’s available on most devices and operating systems and provides a high level of security. The downside? It can result in slower connections. That’s because it uses the double encapsulation process.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). SSL was the encryption protocol VPNs generally used before 2015. It has evolved into TLS for encryption of data traveling to an SSL VPN server. One of the reasons that SSL has been largely replaced in VPNs is due to the large number of vulnerabilities discovered in the protocol.
- Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). PPTP was the earliest of security protocols and first released in Windows 95. It’s fast, but that’s because the protocol provides a low level of encryption.
- Secure Shell (SSH). The SSH protocol isn’t considered especially user-friendly and doesn’t automatically encrypt all of your data. It’s more difficult for users to configure. Plus, fewer providers use this protocol, which limits your choices.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP). This Microsoft-developed protocol is considered highly secure and easy to use, but it doesn’t work as well on platforms other than Windows.
- Internet Key Exchange, Version 2 (IKEv2). This protocol is based upon IPSec. It’s considered quite secure and fast. One downside? It can be blocked by firewalls.
- Open VPN. This is perhaps the most popular VPN protocol. It combines high security and speed. Because it’s open source, numerous third parties maintain and update the technology.
What is a no-log VPN?
A no-log VPN is one that doesn’t collect and use the data that you send through the VPN, such as the websites you visit or your downloads. Because people use VPNs to enhance their privacy, you might think all VPNs would be no-log VPNs. Not so. Some VPN providers collect a minimal amount of your information, such as your email. These VPN providers should list these privacy exceptions in their privacy policy. Norton Secure VPN, for instance, does not log information about where you browse on the Internet. Norton Secure VPN collects other limited data in accordance with the NortonLifeLock Global Privacy Statement and the Product Privacy Notice.
Try Norton 360 FREE 30-Day Trial* – Includes Norton Secure VPN
30 days of FREE* comprehensive antivirus, device security and online privacy with Norton Secure VPN.
Join today. Cancel anytime.
*Terms Apply