8 Factors that Affect the VPN Speed: What Causes VPN to be Slow
^ Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills). Plus taxes $ fees. Limited availability. May not be available in your area.
Will a VPN Slow Down Your Internet?
Most likely, yes: a VPN will slow down your internet. However, the amount your speed is affected depends on the circumstances. How fast your internet was before the VPN, which VPN brand you’re using, and how far away you are from your VPN server can all play a part in your internet speed.
- How does a VPN slow down internet?
- What determines my internet speed?
- Can I test my internet speed?
- Can I increase my internet speed?
- FAQ
Whether you’ll notice the change in speed is difficult to say. With some VPNs, depending on the situation, you might not even notice the difference.
What slows my internet speed when using a VPN?
There are plenty of variables that affect your internet speed when using a VPN service. The most common factors that contribute to your connection speed are:
- The distance between you and your server location
- The type of encryption your VPN uses
- Whether the server you use has bandwidth limitations
Server location
The location of the server you are connecting to has the greatest impact on your internet speed. If you want to make sure your internet runs as fast as possible while using a VPN connection, try connecting to a server that isn’t too far away from you. Use this rule of thumb: the greater the distance between your location and the server you’re connecting to, the higher the chance your internet will run slow.
How far away should my VPN server be?
Some VPNs automatically connect you to the nearest server. But many will give you an option to choose. Generally, if you pick a server that’s on the other side of the world, you will notice a larger difference in internet speed.
While there are some privacy benefits to choosing a different location from where you are, try picking a server that’s located in a neighboring city or state. If you’re not too concerned about your server location and you prefer fast internet, go with something close by.
Encryption
Most of the time, you won’t notice a difference in your internet speed, but sometimes encryption plays a part. For instance, OpenVPN Protocol is the encryption you’re most likely to notice slowing your internet speed.
On the other hand, PPTP is one of the fastest VPN encryptions. Many VPNs use IKEv2 or L2PT/IPSec, which are known for being reliable both for security and for not slowing down your speed too much.
What determines my internet speed?
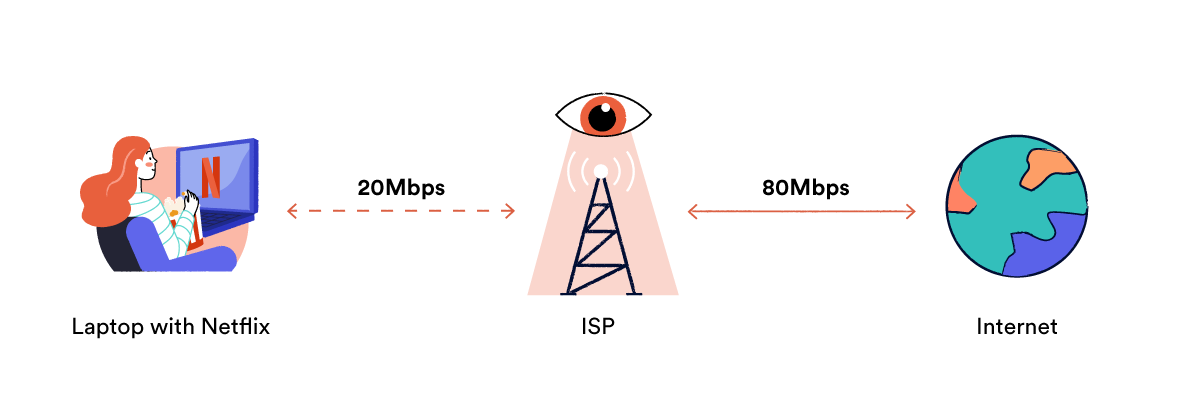
One of the biggest factors is your ISP, or internet service provider. Your speed is influenced by your ISP’s internet connection type (sorry, to those of you on satellite) and by your plan’s speed and data limits. Keep in mind, your plan’s bandwidth is shared across all your devices. When more devices connect and start downloading 4K movies, then the speed will degrade quickly.
Recommended Internet Service Providers
Monthly price
Download speeds
Learn more
Data as of 04/05/2023. Offers and availability vary by location and are subject to change.
* Pricing for some packages are for the first 12 months. Some packages require a 1- or 2-year contract.
† Price per month with Auto Pay & without select 5G mobile plans. Fios plan prices include taxes & fees
‡ Speed may not be available in your area. Paperless billing or prepay required. Additional taxes, fees, and surcharges apply.
^ Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills). Plus taxes $ fees. Limited availability. May not be available in your area.
° Offer available to new qualifying customers. One-time standard installation fee may be due at checkout. Minimum 24-month service term required. Equipment lease fee is $12.99/mo. Taxes apply. Service is not available in all areas. Offer may be changed or withdrawn at any time.
Your router also strongly impacts your internet speed. If it’s outdated, your router isn’t going to be able to keep up. Its location in the home also makes a difference; you’ll want your router close so it can get a strong signal to your devices.
Of course, you’ll want to make sure your modem and all your hardware is working as it should.
Is your internet too slow even before adding a VPN?
Before you accept that buffering wheel as your way of life, check out our tips for improving your internet speed.
8 Factors that Affect the VPN Speed: What Causes VPN to be Slow?
Speed is essential. No one can deny it. One of the essential criteria in choosing a VPN service provider is speed. What, though, differentiates one VPN service from another in terms of speed?
It’s not always simple or obvious to diagnose a sluggish VPN connection. However, if you use the appropriate technique, you can typically overcome the most frequent problems and dramatically increase your performance.
To get the best performance out of your private network connections, you’ll have to deal with a few issues first. Connection speeds can fluctuate, and you may not be able to connect to servers in the system at all. While you’re waiting for the connection to establish, you can unintentionally divulge your real IP address.
So what is the root cause of this problem, and how can it be remedied? In the following part of the article, we’ll go through some of the possible causes of slow VPN connection:
- Routing
- Network Setup
- VPN Protocol
- Server Location
- Encryption Strength
- Server Bandwidth
- CPU/RAM
- Overall Internet Speed
Figure 1. 8 Factors that Affect the VPN Speed
1. Routing
How fast your data travels through the VPN server is directly related to how it is routed via it. Your VPN provider’s method of routing your connection amongst many servers in the same region can have a significant impact. When it comes to routing data via the network, veteran VPN providers have the infrastructure in place to do so more effectively. Inexperienced VPN providers may be unable to adequately do this task. Because of this, you should use a reputable VPN service.
2. Network Setup
In some cases, connecting to Wi-Fi networks rather than LAN connections might result in lower rates. VPNs that are set up through your network rather than the device directly may also result in slower speeds.
In terms of cost, routers are great because they don’t require additional technology or CPUs to be functional. Nevertheless, this means that the router will be slower in its connection speed compared to your older smartphone.
The speed of a wired ethernet connection will always be superior to that of a wireless one. Convenience and quickness aren’t always equal in terms of importance. A good router is a must if you’re not going to be attached. When you have a connection that is significantly faster than 50 Mbps, the differences between wired and wireless Internet become more apparent.
You may want to try connecting your device directly to your network if you are experiencing sluggish VPN speeds when using Wi-Fi. It’s possible to reach twice as fast speeds in some circumstances.
3. VPN Protocol
VPNs are protocol-based. VPN speeds vary depending on the protocol used. OpenVPN, one of the most popular and trustworthy protocols, includes two types: UDP and TCP. Using OpenVPN via UDP is quicker than utilizing OpenVPN over TCP.
Other prevalent VPN protocols, such as PPTP, IKEv2/IPsec, WireGuard, Shadowsocks, and Lightway, offer a quick connection. IKEv2/IPsec, WireGuard, and Lightway are able to strike a balance between speed and security. While PPTP and Shadowsocks may have serious security flaws, both protocols are nevertheless widely used.
4. Server Location
You may not consider the location of your server when selecting a service or how it impacts your connection speed, but it does. For instance, if you use an American VPN while residing in a distant country, the speed will be slower because the data will be traveling over a great distance.
When data travels over extremely great distances, latency (slower speed) rises. In addition, not every data packet you transmit across these extensive distances will reach its intended destination. The longer information must travel, the greater the likelihood of data packet loss.
As a result, your data packets will take longer to reach the website or service you’re attempting to visit if they’re sent from a remote server.
Depending on your current location, many of the best VPN services automatically select the quickest server. If you’re looking for the fastest connection possible, you may hop between servers to see which one works best.
The majority of the time, closer servers will be quicker than distant ones. With a 100 Mbps Internet connection, you may easily get 95+ Mbps on a local server, but only 5-10 Mbps on a server on the opposite side of the globe.
5. Encryption Strength
The stronger the encryption, the slower the VPN connection. Therefore, 128-bit encryption often results in a speedier VPN connection than 256-bit encryption. However, you should be aware that reducing the encryption strength would result in increased susceptibility and make the VPN connection less safe.
The encryption of a data stream requires the inclusion of extra data (this is referred to as encryption overhead). This suggests that encryption eats a portion of your available bandwidth. Consequently, less encryption means more speed.
The encrypted data is what safeguards user privacy and increases data security. Nevertheless, the greater the complexity of the VPN server’s encryption, the more bandwidth it requires, which might create connection speed concerns. While lesser encryption might save time, it is strongly advised to prioritize security above efficiency.
You cannot be certain that a VPN service provider is trustworthy and provides the greatest level of protection. Even worse, 84 percent of VPN service providers reveal the true IP addresses of consumers. Consequently, as a user, you should always test the privacy of your VPN connection to ensure its integrity.
6. Server Bandwidth
So, you have acquired a VPN subscription from a provider. While using it, you may notice that it is really sluggish. One possible explanation for this is that the server is overloaded with concurrent users. This typically occurs while utilizing a free VPN service with limited server capacity and a large number of free users.
It is nonetheless possible with any VPN service, as the bandwidth given to each user is restricted. In general, servers have a limit known as “Server Load”. Server load is the total bandwidth and is dependent on the number of concurrent users. The whole bandwidth is divided among all users, who each receive a portion. When everyone uses it simultaneously, the server experiences difficulty.
The number of users connected to a specific VPN server has a significant influence on your connection speed. If the server is overloaded beyond capacity, the VPN might significantly slow down your Internet connection.
The server might become overloaded regardless of whatever VPN you use, although the issue is more prevalent with cheap ones. Some VPN clients provide information on the server’s available bandwidth and the percentage of capacity that has been utilized. To obtain faster speeds, you should utilize a different server, preferably one with fewer servers and less load.
For instance, if you are utilizing a server with a maximum bandwidth capacity of 1 Gbps and there are 100 users on the server, each user will receive 10 Mbps. Some VPNs, however, use ‘smart’ bandwidth allocation, where they transfer more bandwidth to users who need it more (such as while streaming or downloading large files) and move bandwidth away from those who are not using as much data, resulting in slower connections.
7. CPU/RAM
A VPN does not require disks with a high transfer rate or vast quantities of storage. Since a VPN primarily encrypts data, you will want a powerful CPU to decrypt it. If you are interested in AES encryption, the optimal setup consists of either a CPU or GPUs. Currently, there are servers that offer AES-NI support and have hardware-level performance acceleration.
Due to the time required for data packets to go back and forth, VPN traffic is taking longer than normal. A VPN’s speed may also be impacted when it is encrypted. If your device’s CPU and Internet connection are both fast, its performance will be enhanced.
Generally, it is preferable to utilize a faster CPU if you can improve performance. However, most routers perform poorly due to their RAM. If you increase your RAM, you will have access to more threads, which is crucial given the volume of network activity between devices and torrent sites.
8. Overall Internet Speed
Regardless of how effective the VPN service is, it will be limited by the capacity of the connection you use to connect to the VPN server. If the ISP has a sluggish connection speed, it makes little difference what VPN speeds you have, because best-case scenario, VPN services can only give Internet speeds equal to your ISP’s allotted capacity. In truth, even the fastest VPN services slow down your connection to some degree.
Therefore, you must have a fast Internet connection in order to get satisfactory VPN speeds. You cannot anticipate 50 Mbps speeds if your home connection is barely 10 Mbps.
How to Properly Test VPN Speed?
To test the download speeds, you only need to use a speed test application to compare the percentage difference with and without the VPN. I used the Ookla speed test to evaluate speed since it measures all three essential variables.
There are other additional speed test tools accessible online.
The VPN speed testing procedure is straightforward and can be done in minutes. Follow the instructions below for VPN speed test:
- Firstly, access your VPN account and connect to a VPN server.
- Secondly, navigate to speedtest.com .
- Wait for the connection to be established after clicking Go .
- Read the results of the speed test. Figure 2.Speedtest.com results
- Repeat the procedure without a VPN and make note of the difference.
The smaller the difference, the less of an impact the VPN has on your internet speed and the quicker the VPN.
How Do You Speed Up VPN?
If your VPN connection isn’t as fast as you need it to be, here are several ways to speed it up.
- Connect to a server that is physically closer to your location.
- Connect to a server that isn’t overloaded.
- Try connecting to the VPN using a different protocol.
- Enable split tunneling if available.
- Utilize a cabled connection.
- Close any superfluous background applications.
- Reboot your router and any other devices.
Do VPNs Make Your Internet Faster?
VPNs can improve the speed of various services under specific conditions. ISPs occasionally limit, or artificially slow down, certain types of data; for instance, several large ISPs have throttled entertainment streaming services such as Netflix. If an ISP throttles communication speeds with a particular service, a VPN might evade this throttling since the VPN encryption would prevent the ISP from determining with which services the user is connecting.
Does VPN Speed Depend on Internet Speed?
Yes, VPN speed depends on your internet speed. Your VPN connection can only be as fast as your Internet connection. As security and privacy should always be the VPN’s top concern, performance decreases of 10 to 20 percent are quite typical.
Does Where You Live to Affect Your VPN Speed?
Generally speaking, you will have the best performance by connecting to a server location close to your actual location.
Why? Because it reduces the distance over which data packets must travel to reach the VPN server. To minimize latency and increase performance, it is preferable to avoid servers situated in distant locations.
How to Choose the Best VPN for Speed?
The speed of a VPN may make or break your experience. If the connection is excruciatingly sluggish, you will use it less frequently and detest it each time you do. The first step is to determine which speed data are most important. The three most important measurements are download and upload speeds, as well as ping time.
The first two are exactly what they sound like: the rate at which your device receives and sends data while connected to a VPN. If you often download huge files or stream several movies, you will need a fast download speed. Upload speeds, on the other hand, are crucial if you transfer a substantial volume of data. A nice example is storing your photo backups on the cloud.
Ping time is the amount of time it takes for a single packet of data to go from your computer to the VPN server, to its final destination, and back again. Ping duration is expressed in milliseconds. The better this number is, the lower it is. Real-time applications, such as Skype, voice over IP phones, and online gaming, require a low ping. Which metrics are important to you will depend on your primary motivations for utilizing a VPN.
Once you have determined your metric requirements, search for a VPN provider with the greatest connection speeds for the country to which you wish to connect. Keep in mind that just because a VPN company offers lightning-fast servers in the United States does not guarantee the same in other countries.
- 1. Routing
- 2. Network Setup
- 3. VPN Protocol
- 4. Server Location
- 5. Encryption Strength
- 6. Server Bandwidth
- 7. CPU/RAM
- 8. Overall Internet Speed
- How to Properly Test VPN Speed?
- How Do You Speed Up VPN?
- Do VPNs Make Your Internet Faster?
- Does VPN Speed Depend on Internet Speed?
- Does Where You Live to Affect Your VPN Speed?
- How to Choose the Best VPN for Speed?
Does a VPN Slow Down Your Internet?
Simon Migliano is a recognized world expert in VPNs. He’s tested hundreds of VPN services and his research has featured on the BBC, The New York Times and more.
- Guides
- VPN Features & Troubleshooting
- Does a VPN Slow Down Your Internet?
Our Verdict
Using a VPN will always slow down your internet connection because your data has to travel further to reach its destination. According to our VPN speed tests, a typical VPN will slow down your internet connection by an average of 7% on nearby connections, and 16% on international connections.
Every VPN will slow down your internet connection to some degree because it makes your data travel further.
When you connect to a VPN, your data is encrypted and rerouted through a remote server. At the VPN server, your data is decrypted and sent on to its destination.
Due to the encryption overhead and the distance between you and the VPN server, this process takes longer than browsing the internet without using a VPN at all.
Exactly how much a VPN slows down your speeds depends on multiple factors, including which VPN you’re using, the connection protocol being used, and the location of the VPN server.
Quick Summary: Does a VPN Slow Down Your Internet Connection?
- Using a VPN adds several steps to the process of sending data from your home network to the website you’re visiting. Your data has to travel further to go via the VPN server, which slows down your internet connection.
- Good VPN services should slow your internet connection by a negligible amount. In our tests, a typical premium VPN slows down our speeds by an average of 7% on nearby connections, and 16% on international connections.
- The further the VPN server is from your physical location, the slower the connection will be. Conversely, nearby VPN servers will slow your connection less.
- The protocol used by your VPN service adds additional data to your web traffic, which can slow it down.
- If a VPN server is congested with thousands of simultaneous users, it may respond to your requests more slowly.
- Low-quality VPN services — most commonly free VPNs — are often significantly slower than paid-for VPNs.
Fortunately, there are steps you can take to improve your VPN speeds. These steps apply to all VPN services, although they shouldn’t be necessary if you’re using a top-rated VPN.
Quick Summary: How to Make Your VPN Faster
- Choose a VPN server that’s as close to your physical location as possible.
- If the server you’re using is slow, try switching to find one that’s less congested.
- Where possible, use WireGuard or OpenVPN connection protocols.
- Enable split tunneling to reroute only the most important web traffic.
- Switch to a safe public DNS server to see if it improves your connection speeds.
- If your VPN continues to be slow, consider subscribing to a faster premium service.
In this guide, we’ll explain exactly why a VPN slows down your internet connection, and what steps you can take to reduce the speed loss.
We’ll also suggest ways you can improve your connection speeds, even when you’re not using a VPN.
EXPERT TIP: Not every VPN is capable of delivering fast speeds. If your VPN is frustratingly slow and you’ve tried all of our speed recommendations, you should consider trying a different VPN altogether.
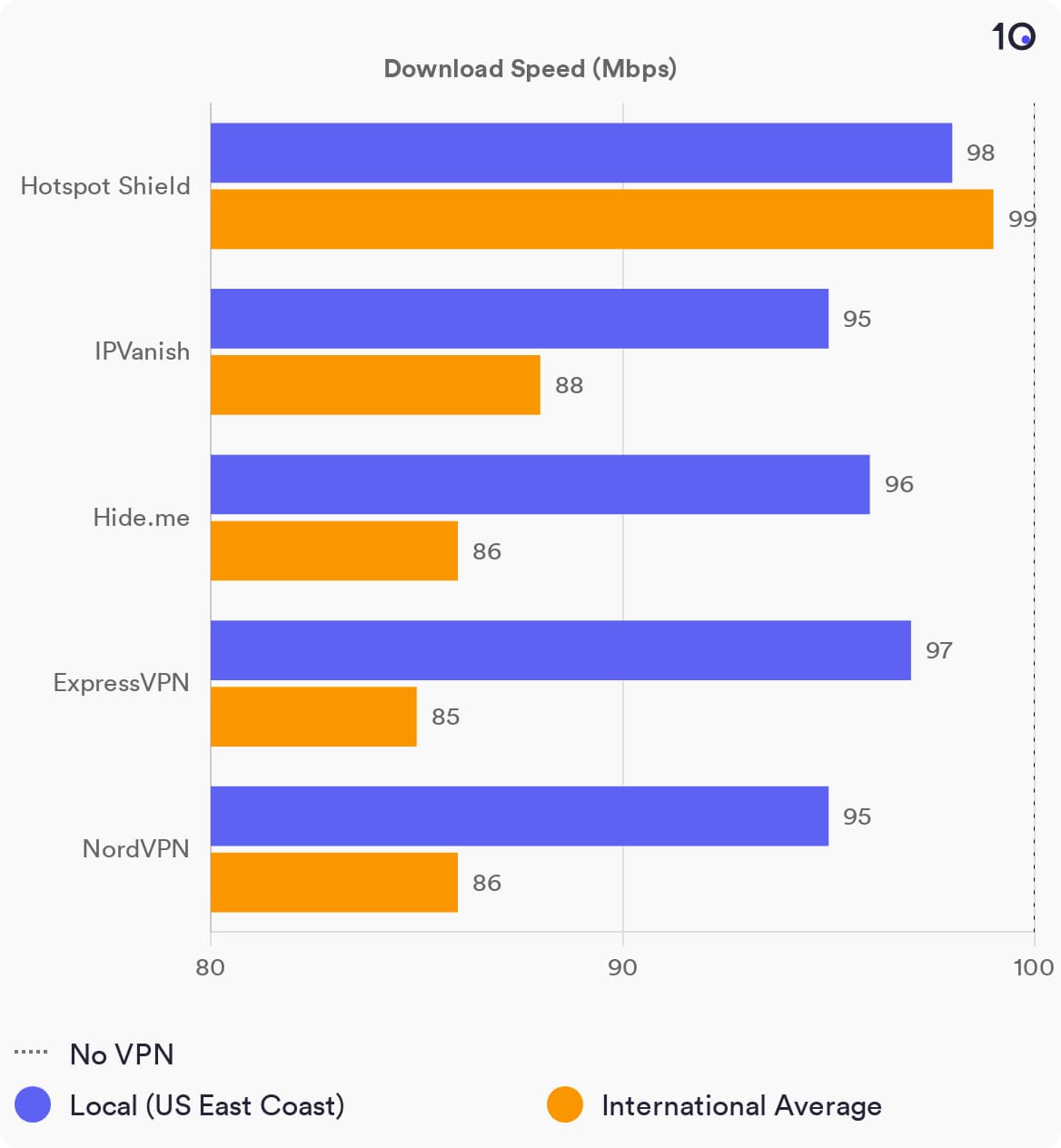
We’ve tested the fastest VPN services and found that Hotspot Shield is consistently the fastest VPN available. It had virtually no impact on our download speeds and delivered much faster results than every other VPN we tested.
What’s In This Guide
- Why Does a VPN Slow Down Your Internet Speed?
- The Factors Affecting Your VPN Speeds
- How to Make Your VPN Faster
- How to Improve Your Connection Speeds In General
- Can a VPN Make Your Internet Speeds Faster?
- How to Test Your VPN Speed
- FAQs
What’s In This Guide
- Why Does a VPN Slow Down Your Internet Speed?
- The Factors Affecting Your VPN Speeds
- How to Make Your VPN Faster
- How to Improve Your Connection Speeds In General
- Can a VPN Make Your Internet Speeds Faster?
- How to Test Your VPN Speed
- FAQs
Why Does a VPN Slow Down Your Internet Speed?
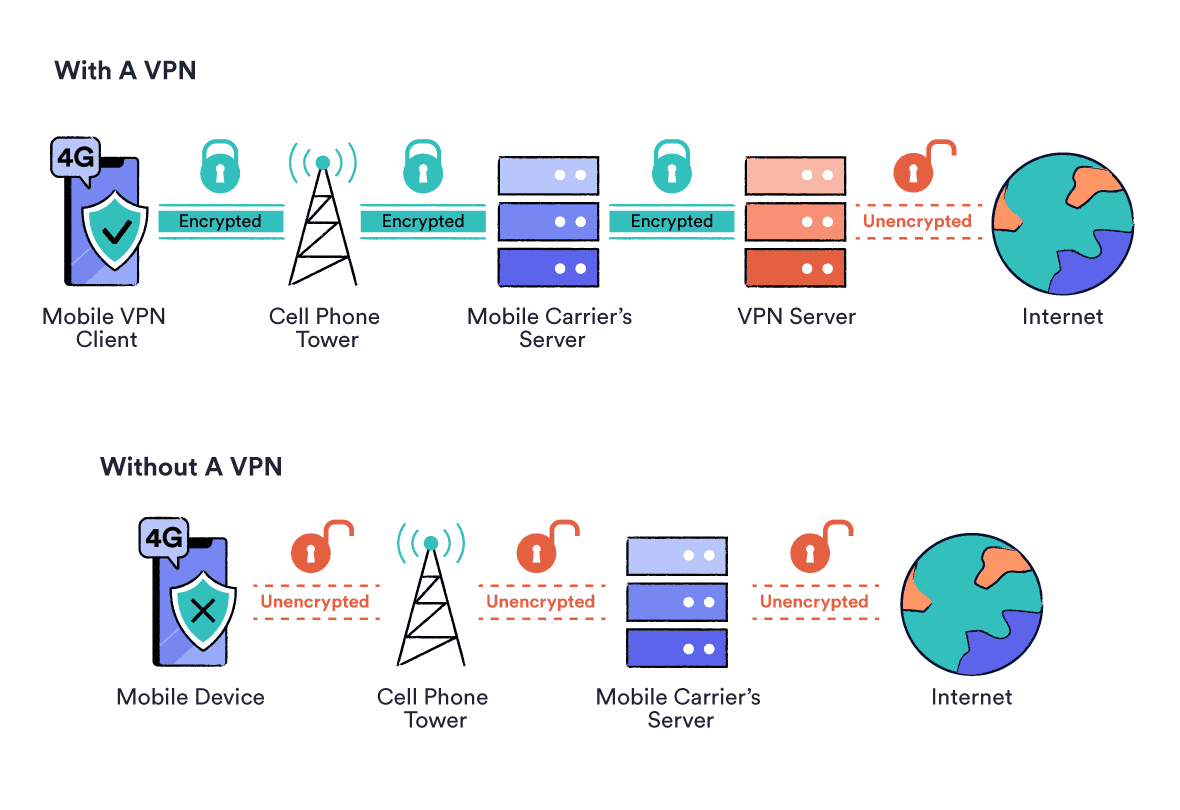
When you connect to a VPN, your data is encrypted and rerouted through a remote server. It has to travel from your home network, through the remote server, and onto its destination, then back again.
How your data travels when using a VPN on a mobile device, compared to not using a VPN.
By rerouting your data, even the fastest VPN will slow down your connection speed somewhat, because your internet traffic has to travel a longer distance between you and its final destination.
VPN services also use encryption to secure your web traffic. This process is carried out using different VPN connection protocols, which can increase the number of packets necessary to transmit the same amount of information.
This is called an “encryption overhead”, and it can also slow down your internet speeds compared to a non-encrypted connection.
How Much Will a VPN Slow Your Internet Speeds?
How much a VPN slows down your connection depends on a number of factors, including the VPN service provider, the server you’re connected to, and the number of people using that server. As a result, VPN speeds can vary wildly.
In our testing, the fastest VPN services only slowed our connection speeds by an average of 7% when connected to a nearby server, and 16% when connected to an international server that’s far away.
NordVPN slowed our speeds by just 5% when connected to a nearby server.
A premium VPN service should only slow your connection speeds by a negligible amount. You should still be able to browse, torrent, and stream content without noticing any significant delays.
The main reason you might experience slow speeds with a premium VPN is if your bandwidth is limited to begin with.
However, there are plenty of low-quality VPN services that are much slower than this. This is typically true of free VPN services with fewer servers and a weaker infrastructure compared to paid alternatives.
In fact, we’ve seen VPNs that slow down your connection by as much as 98%.
The Factors Affecting Your VPN Speeds
In the following sections, we’ll explain more about exactly why a VPN slows down your internet speed, and the factors that can affect it:
The VPN Connection Protocol
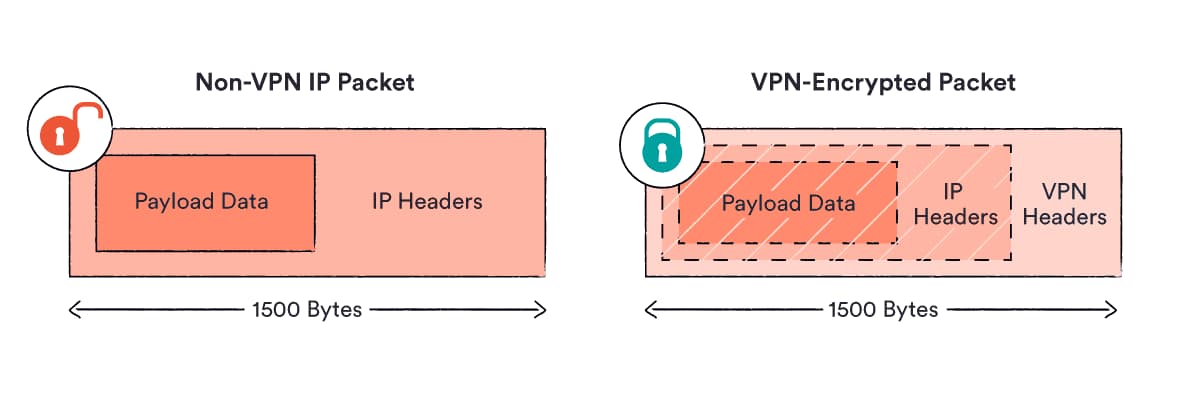
When you send or receive data over the internet, it gets divided into ‘packets’ which contain the data you’re downloading or uploading (known as the ‘payload’). Each packet is limited to a certain amount of data.
In addition to the payload, every packet has to save room for information about where the payload has come from and where it’s going. This additional information is stored in the IP header.
When you use a VPN, the original data packet is encrypted and wrapped in a separate packet (with separate headers) in order to route it to the VPN server.
This process reduces the amount of space in the packet for your payload data. As a result, a file that may have fit into one packet may have to be sent in two packets when you’re using a VPN, as we explain in the diagram below:
When you use a VPN, your data is wrapped in a separate packet.
This is why a VPN’s encryption can also slow down your internet speeds. It’s known as the “encryption overhead”, and it’s also why using a VPN increases the amount of mobile data you consume compared to not using a VPN.
Some VPN protocols add more data to your internet traffic than others, and will therefore slow down your internet connection more.
In the following table, we show which VPN protocols have the largest overheads, and how that may affect your speeds:
VPN Protocol Overhead Speed WireGuard 4.53% Very Fast IKEv2/IPSec 7.88% Very Fast PPTP 8.24% Very Fast OpenVPN UDP 17.23% Fast OpenVPN TCP 19.96% Moderate In our tests, we found that OpenVPN can add an overhead of up to 19.96% to your data. WireGuard, in contrast, only adds 4.53%.
While the VPN protocol you’re using will affect your VPN speeds, the strength of the encryption you’re using will not.
We tested the effect of different encryption ciphers (AES and Camellia) and key lengths (128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit) on data usage and speed. We found that these variables had very little impact on the protocol’s overhead, despite many websites claiming the opposite.
Server Locations
When you use a VPN, your internet traffic takes a detour through a remote server in a location of your choice.
Generally speaking, the further away the VPN server is from your physical location, the slower your connection speeds will be. Nearby servers will typically be faster, because your data simply doesn’t have to travel as far.
When reviewing Private Internet Access, for example, we measured a speed loss of just 5% when connecting to a New York VPN server from New York. This increased to 26% when connecting internationally to a VPN server in South Africa.
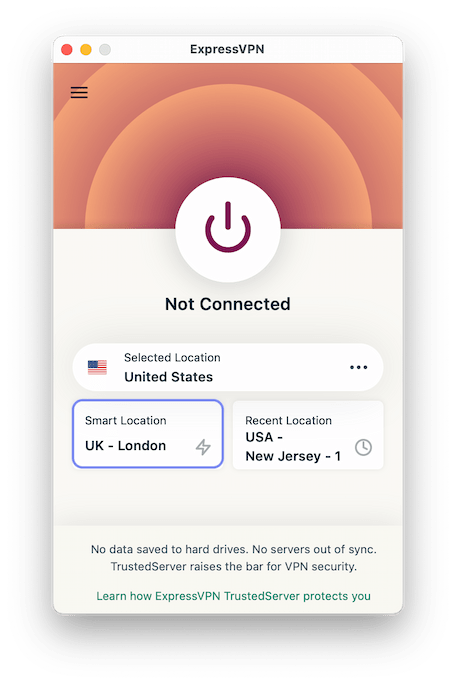
Most top VPN services have a “Quick Connect” or “Smart Location” feature for this very reason. These features connect you to the closest VPN server automatically, improving your chances of getting the best VPN speeds possible.
Using ExpressVPN’s smart location feature can help improve your connection speeds.
Server Load
If lots of people are connected to the same server as you, it may be slow or unresponsive.
VPN servers can get overwhelmed by the number of connections they need to process simultaneously — an issue commonly referred to as server congestion or server load.Large VPN server networks with a wide variety of locations are less likely to suffer from congestion. Free VPN services, on the other hand, tend to have fewer servers and more users, which can lead to slower speeds.
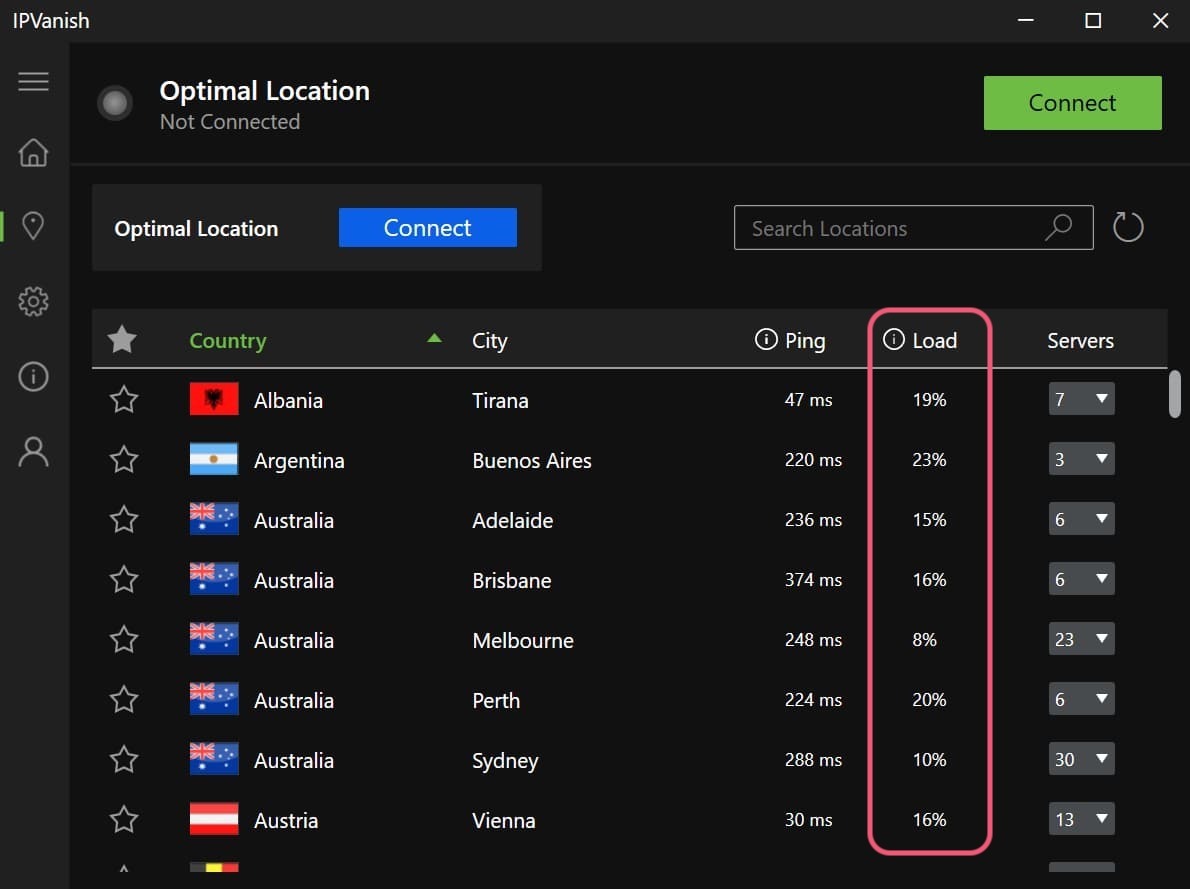
Some premium VPNs, like IPVanish and ProtonVPN, display the load of each server in the application’s menu. This allows you to see which server locations are heavily congested and which aren’t.
IPVanish displays the server load percentage for each VPN server on Windows.
The VPN Service Itself
Not all VPN services are equally fast. Running a secure VPN server network is incredibly complicated, and some providers invest more resources into refining and improving their speeds than others.
As a result, different VPNs can vary wildly in their download and upload speeds, even when using the same server locations and protocols.
We’ve spent hundreds of hours testing the fastest VPN services for this very reason, so we have the speed testing data to back up our recommendations.
A comparison of the fastest VPNs based on our most recent speed tests.
Put simply: if speed matters to you, it’s worth doing your research before purchasing a VPN service. This way, you can ensure that your chosen VPN provider is really capable of the connection speeds you need.
How to Make Your VPN Faster (Stop a VPN From Slowing Your Internet)
Although a VPN will almost always slow down your internet connection somewhat, there are steps you can take to minimize the speed loss, or to compensate for it.
Your server choice, VPN choice, and connection quality all have an impact on your connection speed.
Here’s how to make your VPN faster, or reduce the amount it slows down your connection:
1. Choose a Nearby VPN Server
To minimize your speed loss, we recommend you choose a VPN server that’s close to you geographically.
Same-country connections typically reduce your internet speed by as little as 4%, which would be unnoticeable if you had a reasonably fast connection to begin with.
If you need to use a server in a different country, try to pick the server closest to you. If you’re connecting to the US from Europe, for example, choose a city on the east coast.
2. Choose a Less Congested Server
If too many users are trying to use the same VPN server as you, it will slow down your connection. In this case, try connecting to a different server in the same location.
Aside from server congestion, it’s possible that some servers will be faster than others simply due to the provider’s network infrastructure.
For example, if a VPN service uses virtual server locations, two servers may be in completely different countries even though they assign you the same IP address location. In this case, the closest server to your real location would deliver the fastest VPN speeds.
3. Switch VPN Protocols
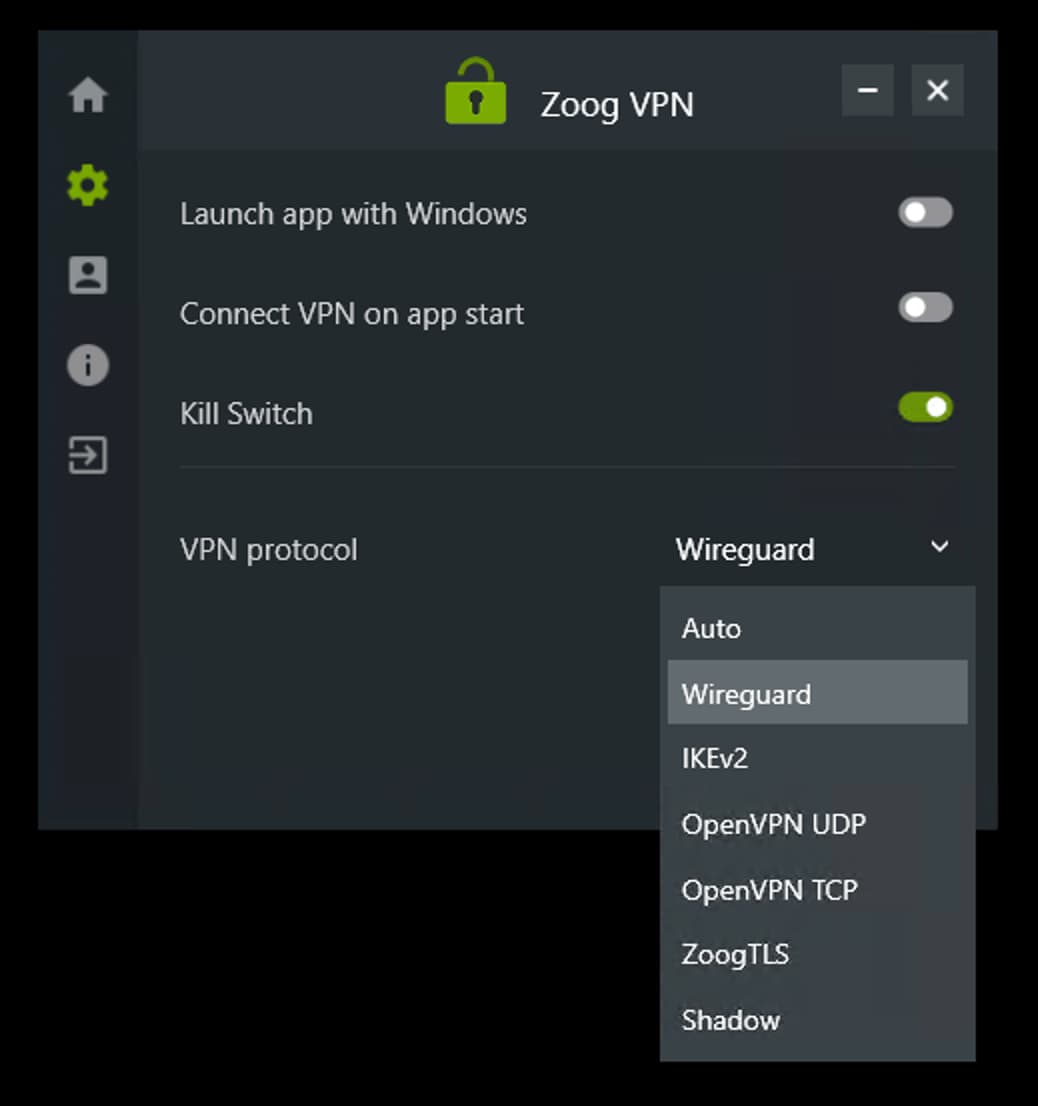
Some VPN protocols are faster than others. If you’re experiencing slow speeds with one protocol, try switching to another protocol and retesting your speeds.
OpenVPN and WireGuard are typically the fastest and most secure VPN protocols available. IKEv2 isn’t quite as fast, but it’s still reasonably secure.
ZoogVPN has an extensive list of protocols on Windows.
PPTP and SoftEther are fast, but they have known security issues, so we don’t recommend using them.
You may also come across VPN services that use proprietary protocols, like ExpressVPN’s Lightway or NordVPN’s NordLynx. Most of these protocols are based on OpenVPN or WireGuard, and are typically the fastest options available.
4. Avoid Free VPNs
Server congestion is a big problem on free VPNs. There is usually a limited number of servers to choose from, and those servers are likely to be overwhelmed by lots of users.
For example, Proton VPN Free — the best free VPN — has 200 free servers in 3 locations. In comparison, ExpressVPN — the top-rated premium VPN — has 3,000 in 94 countries.
There are other reasons to avoid free VPNs, of course: most of them are less private, have weaker security, and are unable to bypass streaming restrictions.
If the very best speeds are a priority for you, you’ll need to subscribe to a premium service.
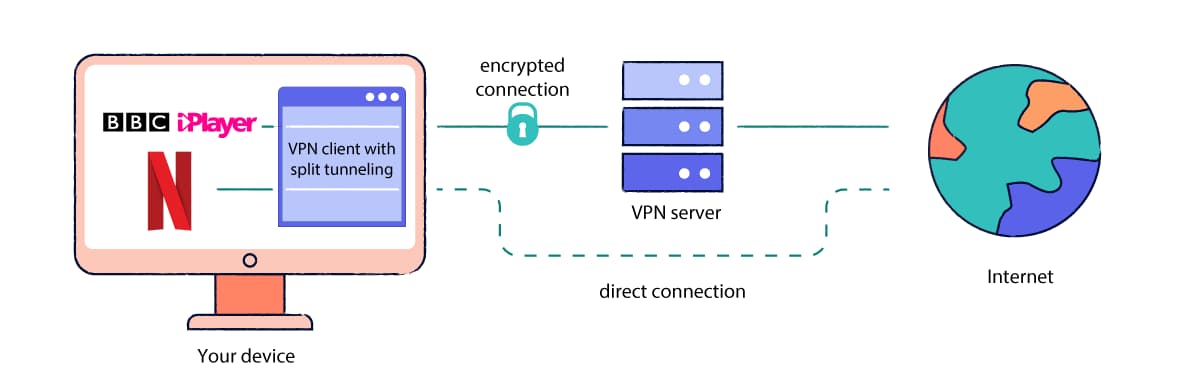
5. Enable Split Tunneling
Split tunneling is a feature that allows you to specify which websites or applications go through the VPN tunnel, and which travel outside of it.
VPN split tunneling routes your excluded traffic outside the encrypted VPN connection.
By running some applications and services outside of your VPN connection, you can reduce the burden on your server and the speed loss you experience as a result.
None of the traffic running outside the VPN will incur the delay of using the VPN server and its encryption.
6. Install VPN Software on Your Device
It’s possible to install a VPN on your router, which protects and reroutes the traffic of all the devices on your home network.
This helps to bypass any restrictions your VPN might have on the number of simultaneous connections you can run. It also enables you to use a VPN with devices that don’t typically support VPN software.
However, a VPN installed on a router will be slower than one installed directly on your device. Unless you have a very high-end router, its processor will not be as powerful as the one on your device, and that will affect your VPN’s performance.
7. Change Your DNS server
A private VPN will typically use its own first-party DNS servers to prevent your ISP from handling your website requests.
If the DNS server is causing a delay, you could try switching your device to a public DNS server to see if that improves your connection speed.
We’ve compiled a list of safe public DNS servers you can use for free with our DNS server tool.
8. Switch VPN Services
If you’re experiencing slow or frustrating speeds with your VPN, it might not actually be able to deliver the speeds you’re looking for.
Some VPN services simply do not have the server network or infrastructure to support fast speeds for thousands of users simultaneously.
If that’s the case, our recommendation is to simply choose a better VPN service. You can start with our reviews of Hotspot Shield and IPVanish — two of the fastest VPNs available in 2023.
How to Improve Your Connection Speeds In General
While there are steps you can take to improve your VPN’s connection speeds, you’re still limited to the physical speed of your home network and the capabilities of your device.
In addition to our recommendations above, there are some steps you can take to improve your device’s memory and bandwidth, which will improve your connection speeds overall (including while using your VPN):
1. Close Background Apps
If you have apps in the background that are constantly sending or receiving data, that can put a strain on your network.
Take a look at your device and see whether there are any apps you’re not using. If so, close them and see whether that makes a difference to your connection speed.
Closing apps will also free up any memory they were using, which may help with your VPN’s performance.
2. Reboot Your Device and Router
Rebooting your device can help to resolve memory leaks or other issues that can accumulate if a machine is running for a long time.
It can also help to resolve any software conflicts, although only if the conflicting software is not set to run automatically on start-up.
Similarly, rebooting your router can help to resolve any issues in that part of your network — especially if you have installed your VPN on your router.
3. Use a Wired Connection
The signal strength on a Wi-Fi connection depends on how close you are to the router. Any walls between you and the router may result in your connection speed slowing down.
A wired Ethernet connection is usually faster than a wireless one, and more reliable, too.
If you’re using Wi-Fi on a desktop computer, laptop, or games console, try connecting a cable to your router instead.
4. Update Your Device
If you’re experiencing slow speeds or other difficulties with your device, it’s always a good idea to check whether any software updates are available.
Updates to the operating system or the network device drivers may improve your connection speeds.
5. Disable Firewall & Security Settings
Your security software could be slowing down your connection. It screens all the traffic between your device and the VPN server, and may be causing a delay.
You can try disabling your security software temporarily to see whether that’s causing your slow connection.
This does present a risk to your security, though we don’t recommend leaving your device unprotected for long.
6. Change Your ISP
It’s possible that your ISP simply isn’t giving you a fast enough connection.
In this case, your connection will be slow even when you’re not using a VPN.
Try using a third-party tool like speedtest.net to see whether your ISP is giving you the broadband speed you’re paying for. If not, consider switching to a different ISP.
Can a VPN Make Your Internet Speeds Faster?
In certain circumstances, using a VPN can actually improve your internet speeds with specific websites or services.
This is only possible if your ISP is deliberately slowing your internet connection to begin with, which is known as ‘ISP throttling’.
ISPs use throttling as a tool to manage the performance of their network. Your ISP may throttle your connection to better distribute bandwidth to other users on the network, or to limit the impact of bandwidth-heavy activities like P2P file-sharing, streaming, or online gaming.
Internet throttling reduces the speed of your connection and your available bandwidth.
Using a VPN stops your ISP from throttling your connection by encrypting your web traffic, preventing your ISP from seeing what you’re doing online.
If the contents of your web traffic and the protocol you’re using are hidden, your ISP can’t throttle your connection based on your activity.
In these circumstances, using a VPN can actually make your connection speeds faster than the throttled speeds you’re experiencing without a VPN.
How to Test Your VPN Speed
The easiest way to measure the impact of your VPN on connection speeds is to conduct a speed test before and after connecting to a VPN server.
To test your VPN speed, follow these steps:
- First, test your connection speeds with your VPN turned off. Visit speedtest.net and write down your download and upload speeds.
- Enable your VPN and connect to the server you’ll use most often. For example, if you’re using a VPN to stream US Netflix, choose a US server.
- Now, visit speedtest.net and measure your connection speeds with the VPN turned on. Make sure the speed test is set to ‘multi,’ which gives the most accurate results on fast connections.
- The result will show you how fast your connection is with your VPN enabled. You can now compare it to your first test to see how much your VPN is slowing down your internet connection.
To find the fastest VPN for your preferred server location, you can also use our VPN speed comparison tool. It allows you to view every VPN’s download speed, upload speed, or ping in eight countries across six continents.
FAQs
Which VPN Does Not Slow Down Your Internet?
Every VPN will slow down your internet to some degree, but the fastest VPNs will have a negligible impact.
VPN services work by encrypting your traffic and sending it through an additional server. Because your data is traveling further and has the added weight of encryption, your connection will almost always be slower than it would without a VPN.
Based on our latest speed tests, Hotspot Shield is the VPN with the least impact on your connection speeds. It reduced our download speeds by just 1% when connected to a nearby server, which is faster than every other VPN we tested.
What are the minimum bandwidth requirements for a VPN?
There are no minimum bandwidth requirements to use a VPN. However, you may need a faster base connection and higher bandwidth if you plan to use the VPN for data-intensive activities like streaming or torrenting.
If you want to stream HD video, for example, you’ll need to ensure your connection is capable of handling that activity without a VPN, first. You should also expect some loss of speed due to the VPN.