256 Bit Encryption – Is AES 256 Bit Encryption Safe in Modern Times
It can happen eight, nine, ten, or 13 times depending on the AES layer.
Why You Should Use AES 256 Encryption to Secure Your Data
Learn about the inner workings of AES 256 encryption, symmetric cryptography, and the most effective encryption algorithm. Before we get to AES 256 encryption, have you ever been curious about how the US government stores its nuclear codes? It could be on a document in an Oval Office vault with the warning “EXTREMELY TOP SECRET.” Who knows? Maybe it’s tattooed on the president’s—never mind. One thing that’s certain is that government secrets and military-grade information are encrypted using a variety of encryption protocols—AES 256 being one of them. And the best part about it is that AES 256 isn’t a privilege of the state alone; it’s a public software that you can use to reinforce your Data, OS and firmware integrity. This article will tell you everything you need to know about your data, AES 256 and everything in between. It will also explain why AES 256 is the closest your organization will ever get to a data security magic wand (and why it’s not one).
What is AES 256?
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256 is a virtually impenetrable symmetric encryption algorithm that uses a 256-bit key to convert your plain text or data into a cipher. That’s a lot of jargon but don’t despair—it gets a lot easier from here.
How Does the AES 256 Encryption Work?
- Divide Information Into Blocks
The first step of AES 256 encryption is dividing the information into blocks. Because AES has a 128- bits block size, it divides the information into 4×4 columns of 16 bytes.
The next step of AES 256 encryption involves the AES algorithm recreating multiple round keys from the first key using Rijndael’s key schedule.
In round key addition, the AES algorithm adds the initial round key to the data that has been subdivided into 4×4 blocks.
In this step, each byte of data is substituted with another byte of data.
The AES algorithm then proceeds to shift rows of the 4×4 arrays. Bytes on the 2nd row are shifted one space to the left, those on the third are shifted two spaces, and so on.
You’re still there. The AES algorithm uses a pre-established matrix to mix the 4×4 columns of the data array.
The AES algorithm then repeats the second step, adding around key once again, then does this process all over again.
What Makes AES 256 Special and Why Should You Use It
That’s enough blabber and technical jargon for today; let’s get to what brought you here in the first place.
Presumably, you want to know what makes AES 256 special, what distinguishes it from the rest and what it brings to your table.
AES 256 brings a lot to your cyber security strategy, including:
1. AES 256 is Unbreakable by Brute Force
Saying that it’s impossible to crack AES encryption is a misnomer. A combination of the perfect brains, the most powerful computer and sheer hacking talent can crack through AES encryption.
But it will take, get this, 10-18 years to do that.
This makes AES 256 and the subsequent data that you protect it with unbreakable for the unforeseen future. Take that, hacker.
However, this is on the condition that you don’t share your cryptographic keys with anyone, your dog included.
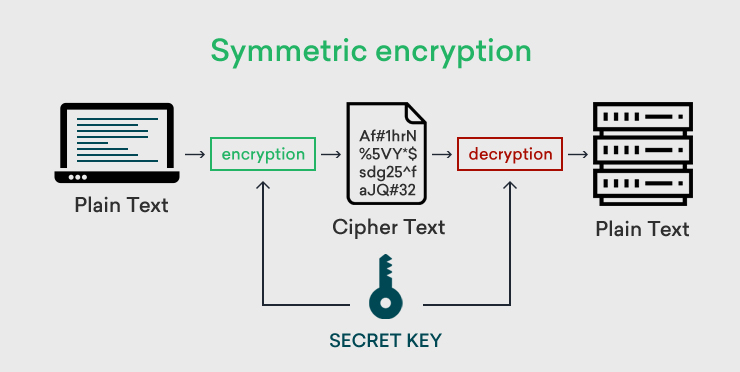
2. AES 256 Uses Symmetric Keys
As you’ve seen, encryption uses a cryptographic key to turn your plain text and data into indecipherable and unreadable text.
Subsequently, it also uses a similar key to decrypt your encrypted data into cipherable text. There are two types of keys in encryption, these are:
- Symmetric keys.
- Asymmetric keys.
A symmetric key is a type of encryption where you use the same key for encrypting and decrypting data.
On the other hand, asymmetric keys use different keys for encrypting and decrypting data. If you’re wondering which one of two is better, there isn’t—both have their uses.
AES 256 is symmetric-based encryption. Not just that, it’s the most capable symmetric encryption available today. Some of the benefits of using symmetric keys are:
- Has faster encryption speed.
- It is good for internal or organizational data.
- It is excellent for encrypting large volumes of data.
- Requires less computational power to run.
3. Stopping a Security Breach from Turning into a Data Breach
If you go around reading breach blogs and reports, you might get the impression that a breach is the end of the world for any business.
You’re not entirely wrong. According to statistics, 60% of small businesses that face a cyber-attack are out of business within six months.
Nonetheless, there is a lot that goes on between your systems getting breached and you going out of business. It all comes down to:
- How soon you identify the security breach.
- Your ability to contain the breach and prevent its spread.
- The contingencies you have in place.
AES 256 encryption allows you to contain the spread of a breach from getting to your data. Take the worst-case scenario and assume that hackers compromise your infrastructure.
With encryption, the chances of this security breach turning into a data breach are significantly reduced.
That’s one less thing to worry about because on one end, your systems are on fire but on another, your data is in safe hands. This possibility reduced the chances of:
- Compliance issues.
- Data theft.
- Ransomware attacks.
4. AES 256 is the Most Secure of AES Encryption Layer
Remember the complex encryption process you read earlier. Well, it doesn’t happen in just a single round.
It can happen eight, nine, ten, or 13 times depending on the AES layer.
This is because we haven’t mentioned two other layers in the AES protocol. They are AES 128 and AES 192.
Both AES 128 and AES 192 are extremely capable encryption layers. So capable that back in 2012, there was an argument about whether AES 256 was necessary given the capability of AES 128.
It’s crazy how fast things change.
In 2022, there is no longer much of a discussion. It’s clear that quantum computers are on the horizon, and AES 256 is the only way to base your secure file transfer infrastructure on a future-proof framework.
By choosing AES 256, you’re going for the gold standard, the best in the game, military-grade and future-proof encryption layer.
What It Will Take for a Hacker to Crack Your AES- Encryption
For a hacker to gain access to your data protected with AES-256 encryption, they will have to try 2^ 256 combinations with a pool of the most powerful computers in the world.
To put this into perspective, this is a number so large it’s more than the number of atoms in the observable universe.
And if by some miracle, a hacker is able to decrypt an AES 256 and wreak havoc on your systems, that will be the second most impressive feat they achieve in their lifetime.
Why? Because they’ll have to live a billion years first to get even close.
Can AES Work in Isolation? No, and Why You Need Managed File Transfer (MFT)
This is one of those few data security pieces that don’t warn of impending doom. It might even have left you with a little hope and the feeling that the good guys are winning for once.
You’re not wrong. AES encryption is probably the best thing to happen to file security since the Firewall.
But there’s a bigger picture; AES encryption cannot exist in isolation. In fact, your AES system encryption is only as strong as its environment and the infrastructure surrounding it.
Hackers may not be able to brute force your AES 256 algorithm, but they don’t give up that fast. They can (and will) still be able to try and:
- Gain access to your AES 256 cryptographic keys.
- Leverage side-channel attacks such as mining leaked information.
- Accessing your data right before and after encryption.
That being said, you need a data security ecosystem around your AES-256 encryption, and for that, look no further than Managed File Transfer (MFT).
The MFT-AES 256 is akin to a Brady Gronkowski duo. In addition to the foolproof nature of your encryption, MFT will bring:
- Strict access control so that no one gets hold of your cryptographic keys.
- Multi-Factor Authentication to prevent unauthorized access to your AES infrastructure.
- Real-time visibility and reports into file access.
To protect your cloud data in transit and at rest, you need both AES 256 encryption and Managed File Transfer (MFT). You need a system that brings you the best of two worlds, and this is where MOVEit comes in.
With MOVEit, you get AES 256 encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), strict access controls, and much more.
For more information, view our MOVEit Transfer Datasheet.
256 Bit Encryption – Is AES 256 Bit Encryption Safe in Modern Times?
How strong is 256 bit encryption? Is AES 256 bit encryption safe? Let’s find out.
When you decide to use encryption for the security of data in your enterprise, one of the first choices that you face is that of encryption strength. There are many options available, with the most popular ones being 128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit encryption. Of course, the safest among them is 256-bit encryption, but sometimes we wonder just how secure it is for the safety of our data. If this question has been going on in your mind too, we’re going to answer it here. Let’s begin with a brief introduction to encryption.
What is 256 Bit Encryption?
256 bit encryption is a security protocol that encrypts and decrypts the data exchanged between the browser and the server using the 256-bit encryption key.
This is the safest digital security solution and hence all the modern algorithms, AES, as well as SSL (Secure Socket Layers) certificates use 256-bit encryption.
The main charm of this encryption is that any intruder who does not possess a decryption key but wants to decrypt the data secured by this encryption needs to try 256 varied combinations to break the cipher code.
All SSL certificates provide 256-bit encryption security which means it processes 2256 varied combinations.
It’s almost impossible to break through 256-bit encryption without the possession of the secret key. Decrypting the same by implementing the trial-error method would take millions of years even for computers to find the right combination.
Usage:
This extremely secure security protocol is used by governments, banks, financial institutions, secret agencies, the military, and other companies. All of them prefer to use AES 256-bit encryption for securing their digital information.
An Introduction to Encryption
Before we go into the subject of 256-bit encryption and its safety, it’ll be a good idea to take a look on what encryption basically is and how it works.
So, the idea behind encryption is to randomize the information/data that would otherwise be in plain text, so no one can make sense of it even if it’s stolen.
This is achieved by running the data along with a secret string of letters through an algorithm, a process usually known as hashing. Here is an example of what simple data in plain text looks like after hashing:
The secret string of letters used in the hashing process is known as a Key. Since encryption is done through a logical process, the data that was encrypted with help of the key can also be decrypted and recovered back into plain text form with its help (except in the case of Public Key encryption, which is a bit more complicated). That’s why the strength of the encryption depends on the length of this Key.
The longer the key, the more time it’ll take to decrypt the data through guesswork-based attacks (i.e. brute force attacks) because the attacker will have to try out a large number of combinations.
Types of Encryptions:
There are three main types of encryptions. They are:
Data Encryption Standard (DES Encryption):
DES Encryption uses a 64-bit encryption algorithm for data encryption. But 8 bits out of 64 bits are utilized in examining cipher errors in the data. So ideally, DES uses 56-bit encryption only which makes it risky to protect sensitive data.
Though DES encryption has lost its place in the market of digital securities, it played a major role in the advancement of cryptographic algorithms.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES Encryption):
AES Encryption uses symmetric key encryption and encrypts blocks of 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit sizes. AES is used in hardware and software all around the globe to encrypt confidential data. It is the best for electronic data protection and is widely used by governments and other financial institutions.
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) Encryption:
RSA also termed Public Key Cryptography uses an asymmetric encryption algorithm. RSA is widely used for secure data transfers, wherein the data is encrypted with the public key which is shared publicly, and the same is decrypted with a private key (mathematically linked with the public key) which lies with the intended recipient only.
Amongst all the above-stated types of encryption, AES 256-bit encryption is widely used and is the most trusted type of encryption. The United States Government, security agencies, secret services, and a majority of companies around the globe use AES for securing their data communications.
Encryption: A bit-by-bit timeline
We just explained the role of longer keys in the strength of encryption. This length of keys is measured in bits, and it continues to increase along with the increase in computing power so that brute force attacks can’t be carried out successfully through a computer powerful enough to break the encryption.
We started with 56-bit keys in the 1970s, which could have 2^56 possible unique combinations. As computing power increased, we shifted to Advanced Encryption Standard in 2001, which allows 128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit keys for encryption.
Today keys of all these 3 lengths are used for the purpose of encryption depending on the sensitivity of the data being protected.
For example, a simple MS Word document is protected with 128-bit encryption; 192-bit encryption is used on websites to protect user data, and 256-bit is used by the banking industry to protect credit and debit card data.
How safe is 256 Bit Encryption?
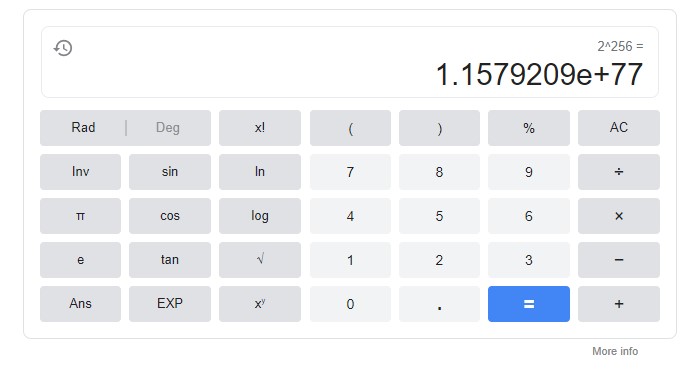
As of now, it’s the safest encryption standard available on the planet, as it can have 2^256 unique combinations. If you’re not good at maths, here’s how many numbers they’re in plain English:
115, 792, 089, 237, 316, 195, 423, 570, 985, 008, 687, 907, 853, 269, 984, 665, 640, 564, 039, 457, 584, 007, 913, 129, 639, 936
The answer is 78-digits. That’s how many possible key combinations can exist in AES-256. More numbers than a modern scientific calculator can calculate. If a computer tries breaking AES 256 via brute force that is the number of unique combinations it needs to try in order to be successful.
256-bit encryption is so strong that it’s also resistant to attacks from a Supercomputer. In case you don’t know about them, supercomputers are computers that can break down huge tasks into multiple smaller chunks and work on them simultaneously with large number of processing cores that they have.
It’s virtually impossible to break AES-256 through brute force attacks, no matter how powerful the computer(s) involved in the process. At present Tianhe-2 (also known as MilkyWay-2) is the most powerful supercomputer in the world, and even that computer would need millions of years to break AES 256 through a brute-force attack. Any attacker would be foolish to even think about attempting something like that.
There have been a few instances of some related-key attacks that were successful in breaking 256-bit encryption (like an attack by Bruce Schneier in 2009); but those attempts were successful because of the incomplete implementation of AES-256. A complete 14-round implementation of AES 256 has not been broken to date.
How 256 Bit Encryption Works?
As stated above, AES is symmetric key encryption. In symmetric encryption, only one single key is used in the entire encryption-decryption process.
Both the sender of the data as well as the receiver of the data use the same key named the session key. The key length which is 256 bits makes this key the largest non-penetrable weapon for hackers and other brute-force attackers.
Symmetric Encryption:
Process:
- When a user accesses a website, the user’s browser and web server mutually select the encryption algorithm for creating a session key. This session key comprises strong 256-bit encryption.
- This key is to be kept secret since it’s used in the encryption-decryption process.
- This session key is encrypted with the SSL certificate’s public key and is later sent to the web server.
- The web server that has the private key of the SSL certificate uses the same for decrypting the session key.
- Once the session key is decrypted by the web server, a secured communication tunnel is established between the user’s browser and the web server.
- Now all the data exchanged between these two parties is encrypted and decrypted using the same session key. On the expiry of the session, the key also expires, thus ensuring complete data security.
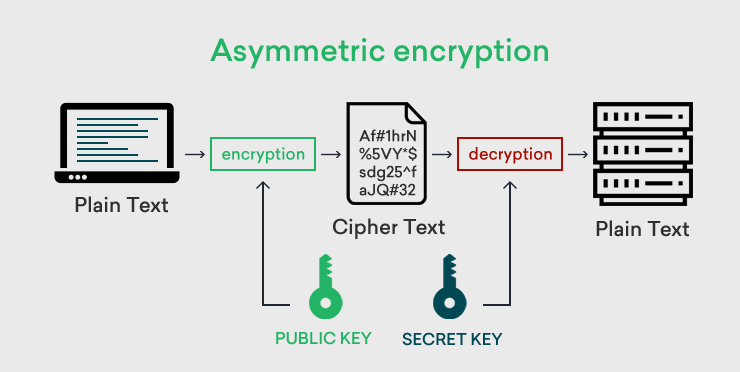
Asymmetric Encryption:
The main difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption is the use of keys. In asymmetric encryption, two different keys which are inter-connected are used in the encryption and decryption process.
The Public Key – encrypts all the data
The Private Key – decrypts all the data encrypted by the public key.
Here, the public key is shared among people but the private key should be kept secret. Compare to Symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption takes time in encrypting data. When someone browses the website, the browser uses asymmetric encryption and gets a public key of an SSL certificate installed on the website. Here, the public key encodes the information and a private key on another side, decodes the information.
Common Uses of 256 Bit Encryption
There are varied uses of this industry-standard 256-bit encryption. They are:
- They are useful in generating symmetric session keys by the browser for initiating and establishing a secured communication tunnel.
- They help in encrypting the data exchanged between the client and the server.
- In the case of the use of email signing certificates, this encryption encrypts the email data storage.
- They also help in encrypting data stored on varied cloud platforms like Google Drive, Microsoft’s Azure, Amazon Web Services, etc.
- They help encrypt sensitive data for all types of industries.
Is 256-Bit Encryption Secure?
256-bit encryption is considered to be the most secure and trustworthy encryption in recent times. It not only ensures data confidentiality but also offers data integrity and data authentication.
Your data is completely secured with 256- bit encryption and hence it’s the most desirable security solution in the digital market.
SSL/TLS certificates use 256-bit encryption irrespective of the brand or validation. This means that a Domain Validation SSL certificate securing the primary domain or an expensive Extended Validation SSL certificate securing the domain use the same encryption security irrespective of the cost.
Such is the power of this encryption security.
The data being protected today with 256-bit Encryption
You can also get an idea of how secure this encryption standard is by the fact that even the US government and its various agencies use only 256-bit encryption to protect their top secrets. All credit card companies, banks and other financial institutions use it to protect the financial data of their customers. It’s used by armed forces around the world to protect their data, which is why it’s also known as Military-grade encryption.
If governments can trust 256-bit encryption with their State secrets, if armies can trust it with their sensitive data and if banks can trust it for protecting the financial information of billions of their customers, then we can definitely trust it for protecting the data of our organization.
Future of 256-bit encryption
Some of you may also be wondering about the future of 256-bit encryption. You may be thinking it is fine that 256-bit encryption is best-in-class today, but will it remain as in the future as computing power increases? Well, the answer is yes. It will remain unbreakable for future years at least. The change in algorithm happens due to rising computing power and its mechanism. The CA/B forum always recommends upgrading encryption strength due to the changing technological environment.
Conclusion
So that was our explanation of how secure is AES 256 bit encryption. The bottom line is that it’s the most secure encryption method that you can use today, and it’ll remain so in the foreseeable future. You can start using it for the security of sensitive data in your enterprise. If you still have any questions in your mind, share them in the comments below and we’ll try our best to answer them.